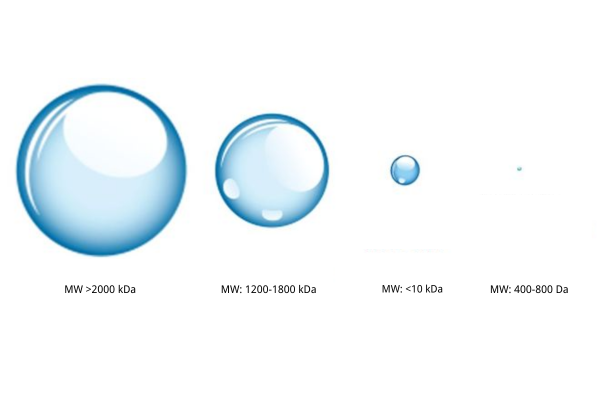
We’ve discussed the many benefits and applications of hyaluronic acid (HA, Hyaluronan), but do you know how it’s made? What production processes are used for the hyaluronic acid found in cosmetics, medical products, and injections? In this article, we’ll explain the two main production methods for sodium hyaluronate and compare the differences between them.
Understanding the Two Methods: Animal Extraction and Bacterial Fermentation
On the market, the production methods for hyaluronic acid can be divided into two categories: animal extraction and bacterial fermentation.
--Animal Extraction
As the name suggests, the animal extraction method involves extracting hyaluronic acid from animal tissues. Common sources include rooster combs, bovine vitreous humor, and fish skin, which are rich in natural Hyaluronan.
As the name suggests, the animal extraction method involves extracting hyaluronic acid from animal tissues. Common sources include rooster combs, bovine vitreous humor, and fish skin, which are rich in natural Hyaluronan.
Process:
The specialized manufacturing process can be divided into the following general steps:
Cleaning: First, fresh animal tissue such as rooster comb is frozen quickly and stored at -20°C. Before processing, they should be washed thoroughly 3-5 times in physiological saline to remove blood and impurities completely. Incomplete cleaning would affect the following purification effect.
Tissue Disruption and Extraction: The washed tissues are pulverized into pulp in a meat grinder and then mixed with 3-5 volumes of 0.1M NaOH solution and stirred at 4°C for 24 hours. The pH should be maintained between 9.0-10.0 since values above would cause rupture of hyaluronic acid molecular chains. The mixture is treated with hydrochloric acid for neutralization, followed by digestion with 0.25% trypsin in a water bath at 37°C for 4 hours.
Purification: The crude extract typically contains impurities that affect the purity and safety of hyaluronic acid. Therefore, purification is a critical step in hyaluronic acid production. Industrially, ethanol precipitation and filtration are commonly used to remove these impurities. However, alternative methods also exist—for details, please refer to this article: 4 Purification Methods of Hyaluronic Acid
Simplified Process:
- Processing and grinding the animal tissue.
- Extracting the hyaluronan through chemical treatment or enzymatic hydrolysis.
- Purifying the hyaluronic acid using methods like precipitation, centrifugation, and filtration.
- Drying and powdering the purified hyaluronic acid.
The main advantage of this process is the higher molecular weight of the product. However, it has disadvantages like limited sources of raw materials, high production cost, and potential risk of animal-related contamination. It is not the mainland process for HA production anymore and is employed mainly in medical aesthetic treatments where products of higher molecular weight are required.
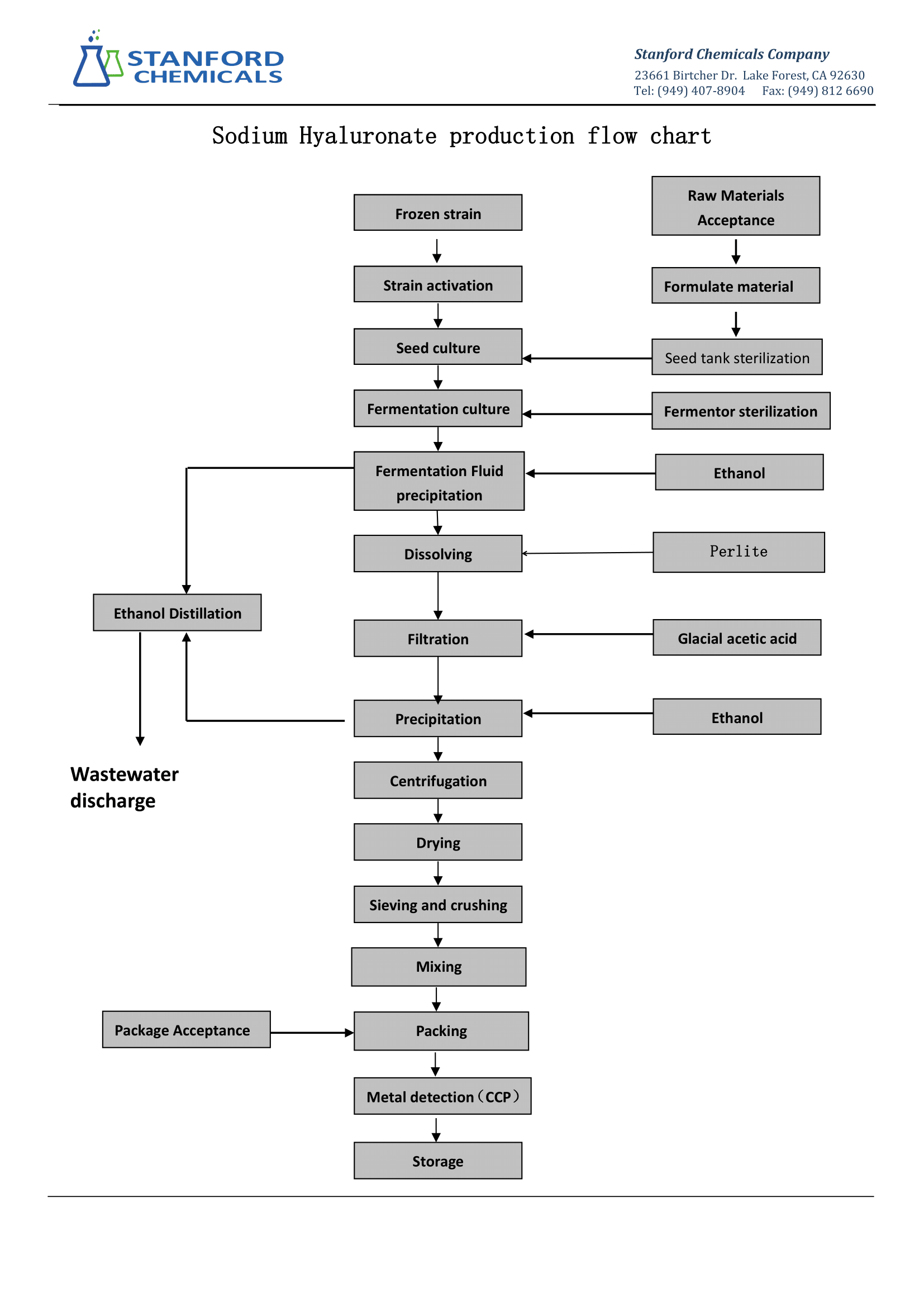
--Bacterial Fermentation
This method uses certain microorganisms to secrete a capsule during growth, and the main component of that capsule is hyaluronic acid. The fermentation process involves feeding the microorganisms nutrients like sugars and amino acids. Common bacteria used are streptococci and lactic acid bacteria.
Process:
- Selecting suitable strains of bacteria (e.g., streptococci).
- Cultivating the bacteria in fermentation tanks, where they produce hyaluronic acid.
- After fermentation, the mixture is filtered, precipitated, and ultra-filtered.
- The hyaluronic acid is then purified and dried into powder form.

Fig 1. Powder with hyaluronic acid
Though these steps may appear simple, they are in fact influenced by several factors. Not only is the selection of appropriate bacterial strains important, but also the culture medium to yield hyaluronic acid is a matter of crucial importance. The medium must offer basic carbon sources, nitrogen sources, vitamins, minerals, and other growth factors for microbes. The medium must be optimized for enhanced production of hyaluronic acid. For example, Amado et al. investigated the optimization of cheese whey medium for hyaluronic acid production by Streptococcus zooepidemicus [1], see Figure 2.

Fig 2. The process demonstrates the production of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus equi in a cheese whey-based culture medium.
In bacterial growth, there are many parameters that can affect microbial growth and yield, thus affecting hyaluronic acid production. They include temperature, pH, aeration, agitation, etc. In most cases, a series of experiments and optimization would be required to determine the optimum culture conditions for hyaluronic acid production.
Comparing the Two Methods: Animal Extraction vs. Bacterial Fermentation
When comparing two processes, we cannot avoid the issues of raw materials, processes, costs, product quality, safety, etc. We will also compare these aspects.
1. Raw Materials
Animal extraction relies on material supplied by animals, and its resources are limited besides raising ethical issues. On the contrary, bacterial fermentation deals with renewable plant-based or synthetic nutrients in a controlled process, hence sustainable.
2. Process Characteristics:
Animal extraction involves the manipulation of biological materials that require high chemical usage. The extraction efficiency is low. Fermentation of bacteria is fully automated and controllable; optimized conditions raise the yield of production.
3. Cost
The extraction from animals is more expensive because the used animal tissues are not very much available, and there is a huge usage of chemicals involved. Handling animal tissues involves more labor and equipment costs due to their complexity. Bacterial fermentation, on the one hand, is less expensive and suitable for large-scale production; to further reduce costs, the fermentation can be carried out on a batch or continuous basis, with raw materials required like sugars and water being low in price.
4. Product Quality and Safety:
Animal extraction uses animal tissues. The possibility, therefore, exists for contamination by the likes of pathogens like bacteria, viruses, or prions, and allergens. Strict safety testing is thus mandatory for all medical and cosmetic applications. Hyaluronan produced by bacterial fermentation, on the other hand, has higher purity. By mimicking the optimum fermentation conditions with great care, and purifying it further, the risk of contamination can be reduced much further, thus being safer. This methodology produces hyaluronic acid-free of all animal components, appropriate for vegetarians and those forbearing animal products.
5. Control of Molecular Weight
The procedure for the extraction of hyaluronic acid from animals does complicate the complete control over molecular weight, which is usually higher. This, in turn, makes it more applicable for products that require high viscosity, such as lubricants or mucosal protectors. Due to bacterial fermentation, better control of molecular weight through adjustments in the steps of fermentation and processing is possible. This flexibility enables various molecular weights for hyaluronic acid to be produced, allowing different applications.
Conclusion
- Animal Extraction: The extraction process is complex, with high costs, low yields, and inconsistent quality. It also poses a risk of contamination from animal sources, making it more suited for small-scale, high-end medical or specialized applications.
- Bacterial Fermentation: This method offers high production efficiency, lower costs, and high product purity. It allows for better control over molecular weight and is ideal for large-scale industrial production. As a result, it is the primary method used for modern hyaluronic acid production.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the common uses of hyaluronic acid?
HA powder is commonly used in cosmetics for its moisturizing and anti-aging properties, in eye drops to provide lubrication, in joint injections to relieve arthritis pain, and as a food additive to enhance texture and moisture.
2. What is the minimum order quantity for hyaluronic acid powder bulk?
SCC offers hyaluronic acid powder in various quantities to meet different customer needs. Whether you’re looking to purchase small bottles or require hyaluronic acid powder in bulk, such as large containers suitable for industrial use, we can accommodate your order.
3. Is Hyaluronic Acid powder safe for use in skincare products?
Yes, HA powder is safe for use in skincare products when used as directed. It is a naturally occurring substance in the human body and is well-tolerated by most skin types.
4. How should Hyaluronic Acid powder be stored to maintain its effectiveness?
To preserve the quality and effectiveness of Hyaluronan powder, it should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Ideally, keep the powder in its original airtight container and tightly sealed when not in use.
Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) is a professional supplier of hyaluronic acid. SCC offers high-purity, high-quality, and safe sodium hyaluronate powder (including food-grade, cosmetic-grade, medical-grade, and injectable-grade). All of SCC’s hyaluronic acid products are made using the bacterial fermentation method, ensuring safety and reliability.
The following figure shows the production process of sodium hyaluronate powder: