Whether for cosmetic or knee injections, receiving hyaluronic acid injections is a major decision. Individuals have the right to access detailed information to make informed choices. As a supplier with 16 years of experience in hyaluronic acid powder, Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) has gathered the most common questions about HA injections.
1. Why Choose Hyaluronic Acid for Injections?
Hyaluronic acid is favored for injections because of its exceptional biocompatibility and lubricating properties. As a naturally occurring polysaccharide in the human body, HA is widely distributed in the skin, joints, and connective tissues, providing superior hydration and lubrication.
In cosmetics, HA is used to:
✓ Fill facial wrinkles
✓ Enhance facial volume
✓ Improve skin elasticity by replenishing moisture for a youthful, smooth appearance
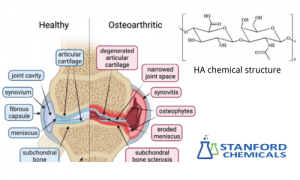
In joint treatments, HA:
✓ Increases synovial fluid viscosity
✓ Improves joint lubrication and shock absorption
✓ Alleviates arthritis symptoms
Thanks to its high safety profile and low risk of immune reactions, HA is a top choice for injectable treatments.
2. Which Body Parts Can Receive Hyaluronic Acid Injections?
HA injections are versatile, targeting multiple areas with distinct purposes and effects. The table below summarizes the main applications of sodium hyaluronate in different areas of the body:
| Injection Site | Primary Use | Expected Outcome |
| Face | Wrinkle filling, contour lifting, lip augmentation | Improved skin elasticity, enhanced facial aesthetics |
| Hands | Volume restoration | Youthful, fuller-looking hands |
| Neck | Skin tightening, fine line reduction | Smoother necklines, reduced wrinkles |
| Joints | Pain relief, improved mobility | Better joint function, reduced discomfort |
3. What Is the Difference between Cosmetic Injections and Joint Injections?
Although both cosmetic injections and joint injections use hyaluronic acid as the primary material, there are significant differences in the types of hyaluronic acid used and injection techniques due to their different purposes and treatment goals. Cosmetic injections are primarily aimed at improving appearance, such as reducing wrinkles, enhancing facial contours, and increasing lip volume.
Common injection sites include the face, hands, lips, and neck - areas that require aesthetic enhancement. To achieve durable yet natural-looking results, cosmetic injections typically utilize high molecular weight (>1000kDa) cross-linked hyaluronic acid, which offers superior filling capacity and longer-lasting effects. However, the formulation must be carefully customized according to the treatment area (for example, lower cross-linking for lip injections) and individual tissue characteristics. Furthermore, cosmetic injections demand highly precise technique from practitioners to ensure natural-looking results while avoiding asymmetry or nodule formation.

In contrast, joint injections primarily focus on relieving pain and improving joint function by enhancing synovial fluid lubrication. The molecular weight selection depends on the arthritis stage. Low molecular weight HA provides rapid anti-inflammatory effects in early stages, while moderate-to-high molecular weight or cross-linked HA is preferred for advanced cases to optimize lubrication and shock absorption. Joint injections require even greater technical precision, as practitioners must accurately deliver HA into the joint space with exact depth and positioning to achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes.
4. How Does the Purity of Hyaluronic Acid Affect Injection Results?
The purity of hyaluronic acid directly affects the safety and efficacy of the injection. High-purity hyaluronic acid contains fewer impurities and potential allergens, which not only reduces the risk of allergic reactions and adverse effects but also ensures its longevity and biocompatibility within the body.
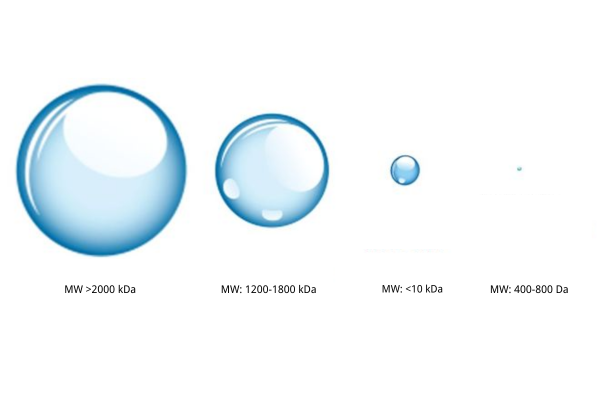
5. How Does the Molecular Weight of Sodium Hyaluronate Affect Injection Results?
The molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate determines its physical properties and therapeutic effects within the body.
| Parameter | High Molecular Weight (>1000kDa) | Low Molecular Weight (<100kDa) |
| Core Advantage | Structural support/Deformation resistance | Rapid penetration/Biological activity |
| Rheological Properties | High G' modulus (Elasticity) | High fluidity |
| Optimal Application | Nasal base/jawline shaping | Epidermal hydration/Dermal regeneration treatments |
| Duration | 12-24 months (requires cross-linking) | 1-3 months (non-cross-linked) |
| Risk Warning | Overfilling leading to a "mask-like" appearance | High swelling risk (high water absorption) |
How to choose?
High molecular weight hyaluronic acid (when combined with cross-linking) is indeed more suitable for deep-layer filling, but its core advantage lies in mechanical support rather than mere water absorption capability. Low molecular weight HA excels in permeability and biological activity but requires attention to its potential inflammatory risks. Clinical selection should comprehensively consider molecular weight, degree of cross-linking, and injection depth, rather than relying on a single parameter.
6. How Does the Solubility of Hyaluronic Acid Affect Injection Results
Choosing the appropriate solubility of hyaluronic acid is crucial for achieving the desired injection outcomes. Highly soluble hyaluronic acid is more suitable for areas requiring fine, natural effects, while low solubility products should be used with caution, typically in conjunction with professional injection techniques to avoid adverse reactions. The injection effects of different solubility HA are as follows: Highly Soluble Hyaluronic Acid:
- Uniform Distribution: Can spread more evenly in the injection area, reducing the risk of local lump formation.
- Natural Filling Effect: Ensures a smooth skin surface post-injection, making it difficult to detect granularity or irregular lumps.
- Balanced Absorption: Aids in the uniform absorption of hyaluronic acid within the body, prolonging maintenance time.
Low Solubility Hyaluronic Acid:
- Easily Forms Granules: May result in noticeable granules or nodules during the injection process, affecting aesthetics.
- Uneven Filling: Can cause localized bulges or depressions, impacting the overall effect.
- Increased Irritation: Local accumulation might trigger inflammation or discomfort.
7. What Are the Advantages of Cross-Linked HA Gels?
Cross-linked HA gel are the preferred material in cosmetic injections because they can provide patients with more lasting and natural aesthetic results. Cross-linked hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels form a stable cross-linked structure between HA molecules through chemical or physical methods. This cross-linked structure enhances the mechanical strength and durability of the HA hydrogel, slowing its degradation rate within the body and extending the longevity of the injection effects. Moreover, cross-linked HA hydrogels can better maintain their shape after injection, reducing diffusion and migration. What’s more, the cross-linking process can further purify HA, removing impurities and lowering the risks of immune reactions and allergic responses.
8. How Long Do Hyaluronic Acid Injections Last for the Knee and Face?
The duration of HA injections depends on the treatment area and individual factors such as metabolism, activity level, and the specific HA product used. Generally, the duration is as follows:
| Injection Site | Purpose | Duration | Influencing Factors |
| Knee Joint | Alleviate joint pain, improve joint function | 6 months to 1 year | Degree of joint degeneration, activity level, overall joint health |
| Face | Fill wrinkles, enhance facial contours, increase lip volume | 6 months to 2 years | Injection area, skin quality and age, lifestyle factors (e.g., sun exposure, smoking) |
9. What Are the Side Effects of Hyaluronic Acid Injections?
Due to the biocompatibility of hyaluronic acid (HA), injections of HA are generally considered safe. However, like any medical procedure, they may produce potential side effects. Common side effects include: Local Reactions:
- Redness and Swelling: Temporary inflammation at the injection site.
- Pain and Tenderness: Mild discomfort during and after the injection.
- Bruising: Minor bruising may occur at the injection site.
Rare Side Effects:
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions, including itching, rash, or hives.
- Lumps and Bumps: Small lumps or nodules may form subcutaneously, which might require massaging and, in extremely rare cases, medical intervention.
- Infection: As with any injection, there is a slight risk of infection at the injection site.
- Vascular Occlusion: A very rare but severe complication where HA is inadvertently injected into a blood vessel, potentially causing tissue necrosis or vision problems if it occurs near the eyes.
Mitigation Measures:
- Experienced Practitioners: Ensure that injections are performed by qualified and experienced medical professionals to minimize risks.
- Proper Disinfection: Maintain a sterile environment to reduce the risk of infection.
- Patch Testing: Conduct skin tests on individuals known to be allergic to HA or related substances.
Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) is a professional supplier of hyaluronic acid. SCC offers high-purity, high-quality, and safe sodium hyaluronate powder (including food-grade, cosmetic-grade, medical-grade, and injectable-grade). All of SCC’s hyaluronic acid products are made using the bacterial fermentation method, ensuring safety and reliability.