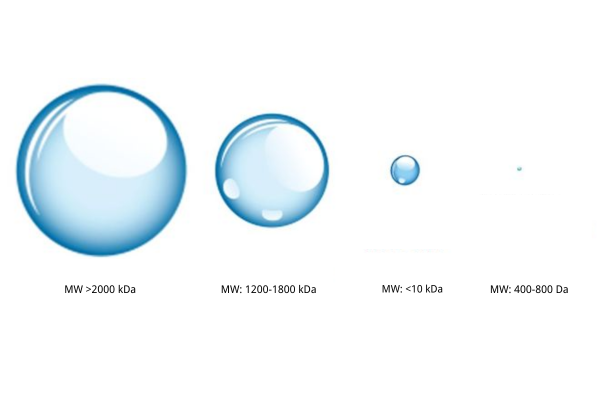
Hyaluronic acid and glycerin are both popular moisturizing ingredients in skincare products. But which offers better hydration? Let's dive into some of the main differences.
Understanding Hyaluronic Acid and Glycerin
--Hyaluronic Acid
If you've ever researched skincare ingredients, you have likely stumbled upon hyaluronic acid, also known as HA. Unlike most skincare ingredients, hyaluronic acid occurs in our skin. It is a sugar molecule that appears in the connective tissues of the body, eyes, and skin.
Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid:
- Powerful Moisturizer: HA has an intense capacity to attract and hold water, thus providing the skin with deep hydration.
- Improves Skin Elasticity: HA penetrates the dermis layer, which helps the skin retain elasticity. As a result, it tends to sag less and droop less often.
- Reduces Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Hyaluronic acid helps replenish skin moisture and maintain healthier skin barriers, and thereby, does an effective job of reducing the appearance of dry lines and fine wrinkles, offering some anti-aging benefits.
- Stimulates Skin Repair: Hyaluronic acid possesses anti-inflammatory properties, which can help in the process of skin repair and regeneration, thus reducing inflammation and irritation.
- Skin Barrier Protection: It forms a kind of barrier on the skin's surface and inhibits water loss. It protects your skin from environmental damage, such as pollution and UV rays.
Besides skincare routines, hyaluronic acid is also valued in many medical and health fields due to its many properties, which can moisturize, lubricate, and repair. It provides lubrication to joints, helps reduce dry eyes, and speeds up the healing of wounds.
Fig 1. Comparison of skin effects before and after using hyaluronic acid
--Glycerin
Glycerin, also known as glycerol, is an odorless, colorless, thick liquid. It is the simplest form of polyol compound that occurs naturally in vegetable oils and animal fat. Glycerin exhibits strong hygroscopic activity by attracting moisture from the environment towards the skin and into it. Benefits of Glycerin:
- Moisturizer: Glycerin prevents the skin from losing its moisture content. Dryness and rough skin are prevented by glycerin.
- Skin Repair: It repairs the skin barrier and therefore reduces dryness, flaking, and roughness. The overall skin health improves.
- Lubricating Effect: Glycerin possesses excellent lubricating properties; it reduces friction, hence soothing discomforts. It finds applications in skincare products and also in medical lubricants like oral ulcer protectants and lubricating eye drops.
- Promotes Wound Healing: Glycerin promotes wound healing due to its moisturizing action, which helps in maintaining a moist environment for wounds. This helps in faster healing of the wound and minimizes post-healing scar formation. This is the reason for its common inclusion in various ointments for wound care.
Hyaluronic Acid vs Glycerin: Differences in Hydration Mechanism and Effectiveness
Going back to the original question, as moisturizing ingredients, how do their hydration mechanisms and effectiveness differ?
--Hydration Mechanism
Hyaluronic acid can provide a barrier layer to the skin mainly because of its larger molecular structure, the molecule forms a locked structure that holds moisture. It can also be penetrated into the skin to absorb atmospheric moisture. The absorption and moisturizing effects of hyaluronic acid vary depending on its molecular weight. High-molecular-weight HA keeps itself at the surface of the skin to afford immediate hydration, whereas low-molecular-weight HA goes deeper into the skin and can provide longer-lasting hydration. Glycerin, as a humectant, absorbs moisture from the environment and draws it into the skin layers, while also preventing water loss. Glycerin has good penetration, reaching into the stratum corneum to help keep the skin soft and supple.
--Hydration Effectiveness
Studies have compared the water absorption and retention capabilities of hyaluronic acid and glycerin (see Figures 2 and 3). 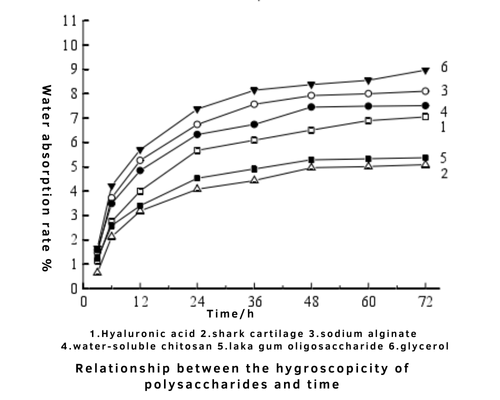
Fig 2. Relationship between water absorption of polysaccharides and time
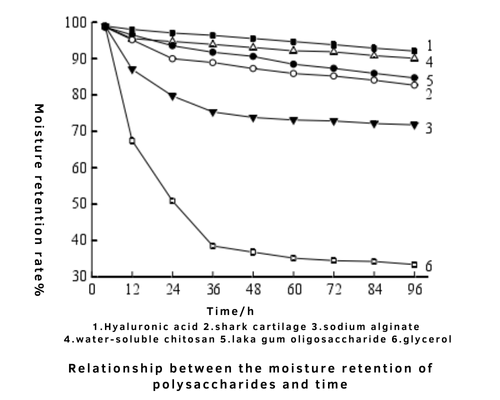
Fig 3. Relationship between the moisture retention of polysaccharides and time
Based on these experimental results, hyaluronic acid may not have the best moisture absorption, but it excels in moisture retention. Conversely, glycerin is excellent at absorbing moisture but not as effective at retaining it. Therefore, if you want to keep your skin hydrated over the long term and improve its moisturizing capacity, products containing hyaluronic acid are the better choice. Additionally, glycerin can sometimes feel sticky and "heavy" on the skin, making it less suitable for oily or acne-prone skin types. Hyaluronic acid, on the other hand, is lightweight and non-sticky, making it the ideal moisturizer for oily skin types.
Conclusion
Though hyaluronic acid and glycerin both offer merits, their choice depends upon your skin type and specific needs. Hyaluronic acid is perfect for those seeking deep, long-lasting hydration without the feeling of heaviness. Not only does hyaluronic acid hydrate the skin, but it also improves elasticity, decreases fine lines, and generally keeps the skin in good health. Glycerin works better just for hydration and barrier repair and is also generally more suitable for dry or sensitive skin. Both of these ingredients may play a beneficial role in a skincare routine, yet the differences between them might help you decide on your particular skin concerns.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a premium supplier specializing in sodium hyaluronate powder. Our product range includes:
- Cosmetic Grade Hyaluronic Acid
- Food-Grade Hyaluronic Acid
- Injection Grade Hyaluronic Acid
- Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid
- Zinc Hyaluronate
Our sodium hyaluronate powder is Ecocert certified and produced under strict ISO 9001 and GMP standards. All products are fermentation-based, non-animal origin, non-GMO, and carry no BSE/TSE risk.
Related articles:
High VS. Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid
Top 10 Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid