- Home
- Pharmaceuticals
- 040-000-290 Piperaquine, CAS 4085-31-8
040-000-290 Piperaquine, CAS 4085-31-8
| Synonyms | Piperaquine Phosphate, Sotalol Hydrochloride, Piperaqu, Piperaquinoline |
| Keywords | Malaria, artemisinin, Artemisia Annua Extract, COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 |
| Related products | Artemisinin, hydroxychloroquine |
Stanford Chemicals Company is a Piperaquine supplier in USA. We offer the small Piperaquine phosphate sample and bulk powders.
- Description
Description
Piperaquine Specifications
| Product Name | Piperaquinoline |
| CAS Registry Number | 4085-31-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C29H32Cl2N6 |
| Molecular Weight | 535.51 g/mol |
| Purity | >99.0 % |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | highly active against chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax |
Piperaquine Description
Piperaquine is an antiparasitic drug used in combination with dihydroartemisinin to treat malaria. It is a bis-quinoline compound that inhibits the vitro growth of P. falciparum isolates from malaria-infected patients with IC50s ranging from 11.8-217.3 nM. Piperaquine was developed under the Chinese National Malaria Elimination Programme in the 1960s and was adopted throughout China as a replacement for the structurally similar antimalarial drug chloroquine.
Piperazine phosphate has also recently become a potential drug against COVID-19.
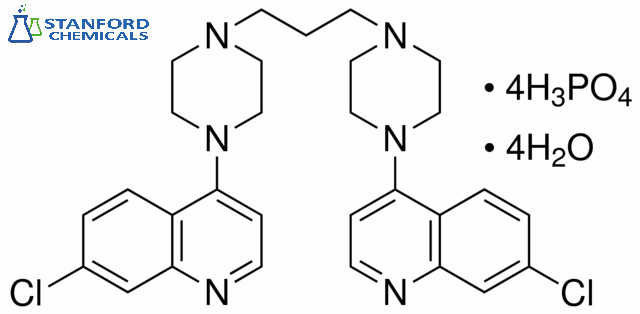
Piperaquine
Piperaquine Applications
- Used in combination with artemisinin to treat malaria
- Potential drug against SARS-COV-2
Piperaquine Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which piperaquine inhibits the heme detoxification pathway is unknown but is expected to be similar to that of chloroquine. It acts by accumulating in the parasite’s digestive vacuole and interfering with the detoxification of heme to hemozoin.
Piperaquine Mechanism Side Effects
While piperaquine is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects. Common and serious side effects include:
Common Side Effects:
Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Headache: Mild to moderate headaches can occur.
Dizziness: Some patients may experience dizziness or light-headedness.
Although clinical trials have found no evidence of cardiotoxicity, the World Health Organization recommends against the use of piperaquine in patients with congenital QT prolongation or who are taking other drugs that prolong the QT interval.
Additionally, studies of piperaquine in monkeys and dogs have shown some hepatotoxicity and reversible suppression of leukocytes and neutrophils.
Reference:
- Akoachere, M., Buchholz, K., Fischer, E., et al. In vitro assessment of methylene blue on chloroquine-sensitive and -resistant Plasmodium falciparum strains reveals synergistic action with artemisinins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49(11), 4592-4597 (2005).
- Davis TM, Hung TY, Sim IK, Karunajeewa HA, Ilett KF (2005). “Piperaquine: a resurgent antimalarial drug”. Drugs. 65 (1): 75–87.
- Haldar K, Bhattacharjee S, Safeukui I (2018). “Drug resistance in Plasmodium”. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 16: 156–170.