Hyaluronic acid (HA), initially extracted from bovine vitreous humor, is a natural polysaccharide. It naturally exists in our bodies and is widely distributed in the eyes, joints, skin, umbilical cord, and other tissues. It plays many important roles in the human body. This article will explain in detail the top 10 benefits of HA on the human body.
1. Hyaluronic Acid for Skin: Moisturizing and Anti-Aging
Hyaluronic acid is a component of the dermis layer of the skin, capable of retaining 100 times its weight in water. This is the source of its powerful moisturizing ability. Therefore, using HA can keep the skin hydrated, effectively improving dryness, roughness, and peeling. For the skin, hyaluronic acid is not just a moisturizer; it also effectively combats aging. This is because HA can fill the gaps within the skin, smoothing out wrinkles and fine lines. Additionally, it increases skin elasticity, making the skin firmer and reducing sagging. As we age, supplementing with HA is a highly effective anti-aging strategy.
Read more: Hyaluronic Acid Powder: The Acne-Prone Skin Savior
2. Hyaluronic Acid for Facial Contours: Filling Hollows and Smoothing Wrinkles
HA is a primary choice in cosmetic procedures for enhancing facial contours. Hyaluronic acid injections can fill in sunken areas of the face, such as the cheeks, temples, and chin, creating smoother and more defined facial lines. Additionally, it can smooth deep wrinkles, such as nasolabial folds and crow's feet, lifting sagging facial skin and restoring a youthful, firm appearance.
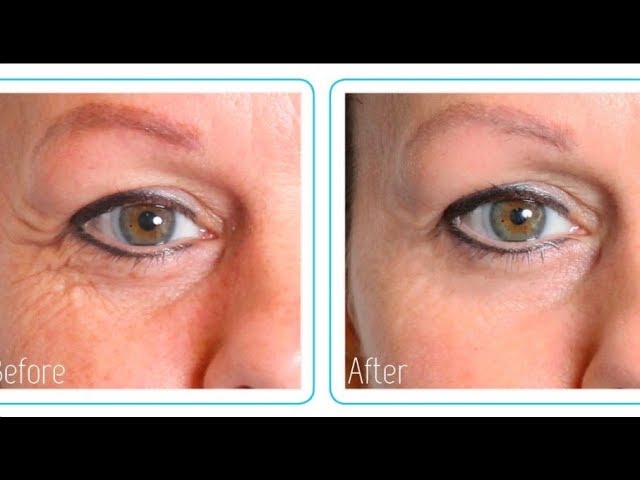
Fig 1. Hyaluronic Acid for Facial Contours: Before and After
3. Hyaluronic Acid for Lips: Safe Lip Augmentation
Injectable-grade hyaluronic acid is a common method for lip augmentation. By injecting HA, the appearance of the lips can be significantly improved, making them fuller and more defined. Additionally, HA injections can effectively reduce fine lines and wrinkles on the lip surface. Even without injections, applying HA directly to the lips has benefits. Because of its moisturizing properties, it helps the lips retain moisture, preventing dryness and cracking. Moreover, its anti-inflammatory properties can alleviate symptoms of lip inflammation, reducing redness and discomfort.
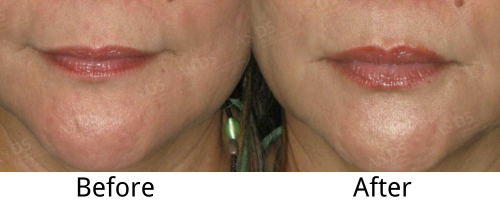
Fig 2. Injectable-grade HA on Lips: Before and After
Read more: Fuller Lips Made Easy: The Power of Hyaluronic Acid
4. Hyaluronic Acid for Wound: Promoting Healing and Reducing Scars
The strong moisturizing capability of hyaluronic acid is not only beneficial for the skin but also accelerates wound healing. It forms a protective film, locking in moisture and preventing the wound from drying and scabbing. Additionally, HA has anti-inflammatory properties, reducing inflammation at the wound site. Another important role of HA in wound healing is promoting skin regeneration. It facilitates cell migration and proliferation, crucial steps in the healing process. Moreover, HA can reduce scar formation by promoting collagen synthesis, which enhances the strength and elasticity of new tissue, thus minimizing scarring. 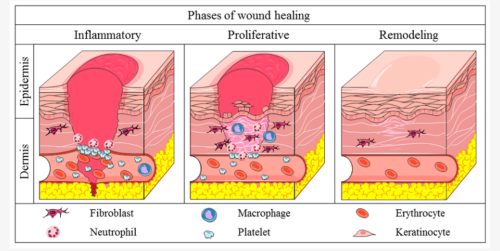
Fig 3. The three phases of wound healing
Read more: Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid and Wound Healing
5. Hyaluronic Acid for Eyes: Relieving Dryness and Protecting the Cornea
Hyaluronic acid can keep the surface of the eyeball moist, significantly relieving dryness, irritation, and discomfort. Thus, eye drops and gels containing HA are widely used to treat dry eye syndrome and other eye discomforts. In addition to relieving dry eye symptoms, hyaluronic acid has numerous benefits in eye surgeries. It forms a protective film, preventing dust, bacteria, and other harmful substances from damaging the cornea. In cataract and other intraocular surgeries, hyaluronic acid serves as a filling material, helping maintain the stability of intraocular structures and protecting intraocular tissues. Furthermore, it can be used as a surgical aid, reducing intraoperative damage and promoting postoperative healing.
Read more: Sodium Hyaluronate for Dry Eyes and How It May Increase Intraocular Pressure
6. Hyaluronic Acid for Joints: Relieving Pain and Delaying Degeneration
Hyaluronic acid has a significant effect on alleviating joint inflammation. It is a crucial component of synovial fluid, providing excellent lubrication. It reduces friction between joint surfaces, protecting cartilage and reducing pain and discomfort during joint movement. By improving lubrication and reducing pain, HA can enhance joint flexibility and stability, reducing stiffness. Additionally, it protects and repairs joint cartilage, slowing its degeneration. 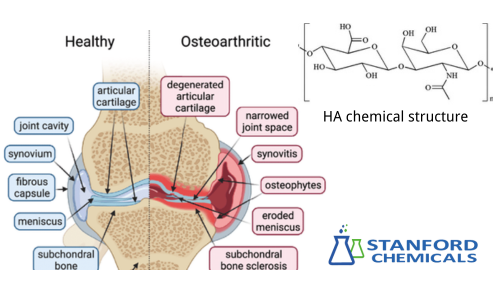
Fig 4. Anatomy of the healthy and osteoarthritic knee joint[i]
Read more: Hyaluronic Acid VS. Glucosamine VS. Chondroitin: Which Is Best for Joints?
7. Hyaluronic Acid for Bones: Preventing Osteoporosis
Hyaluronic acid is a key component of the bone matrix, playing an important role in bone health. It provides structural support to bones, promoting the formation and maintenance of the bone matrix. In the healing process of fractures and bone injuries, HA also plays a crucial role. It promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts, accelerating bone regeneration and repair, thus shortening the healing time. Moreover, its anti-inflammatory properties reduce inflammation after bone injuries. Hyaluronic acid helps prevent osteoporosis by promoting the deposition of minerals (such as calcium and phosphorus) in bones, increasing bone density and strength.
8. Hyaluronic Acid for Hair: Preventing Dryness and Enhancing Strength
Hair that lacks moisture becomes dry and frizzy. Hyaluronic acid, with its moisturizing ability, helps hair retain moisture, making it softer and smoother. Similarly, it keeps the scalp hydrated, preventing dryness and flaking, and promoting a healthy environment for hair growth. Moreover, HA enhances hair strength and elasticity, reducing breakage and split ends. Its antioxidant properties also benefit hair health by neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress damage, maintaining the health of the hair.
9. Hyaluronic Acid for Brain: Protecting Nerves
Hyaluronic acid plays a significant role in neuroprotection. It protects nerve cells from external damage, reducing apoptosis and injury. Additionally, hyaluronic acid is an important component of the brain's extracellular matrix, providing structural support and maintaining the health of the extracellular matrix. Researchers have noticed the potential of HA in improving cognitive function. By enhancing the health and function of nerve cells, HA may support learning and memory. Its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects could also help reduce age-related cognitive decline. 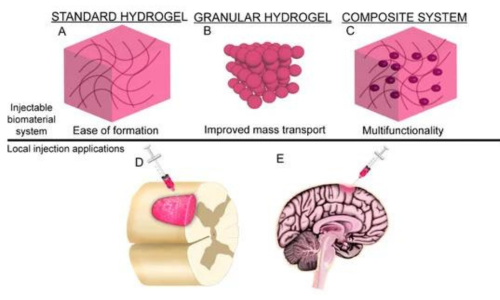
Fig 5. Different forms of HA scaffolds[ii]
10. Hyaluronic Acid for Teeth: Protecting Gums
Hyaluronic acid significantly protects and repairs gum tissue. It can keep gum tissue hydrated and enhance the barrier function of the gums, preventing bacteria and toxins from invading. Additionally, HA has excellent anti-inflammatory effects. It can inhibit the release of inflammatory factors, alleviating gum inflammation and periodontal disease. The ability of hyaluronic acid to promote wound healing plays a crucial role in accelerating the healing of oral injuries and post-surgical recovery. Therefore, after tooth extractions or implants, HA can speed up wound healing and reduce postoperative complications.
Conclusion
Hyaluronic acid's multifaceted benefits span across various aspects of health and beauty, from maintaining skin hydration and enhancing facial contours to promoting joint and bone health. Its unique properties make it an invaluable component in medical treatments and cosmetic applications, improving overall quality of life. As research continues to uncover new potential uses, hyaluronic acid is set to remain a cornerstone of health and wellness.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is an excellent supplier of Sodium Hyaluronate Powder. We provide cosmetic-grade, food-grade, medical-grade, and injection-grade sodium hyaluronate powder. For more information about these materials, please check out our home page.