Does Chondroitin Sulfate Help with Arthritis
As people age, many start to experience discomfort in their joints, with some developing symptoms of arthritis. Arthritis is a common degenerative disease characterized by the wear and tear of joint cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited movement. Among the many supplements available to alleviate arthritis symptoms, chondroitin sulfate has gained popularity as a key ingredient in joint health products. But the question remains: Does chondroitin actually help with arthritis?
The Mechanism of Chondroitin Sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a naturally occurring substance found in the cartilage of the human body. Its primary function is to help maintain the elasticity and hydration of cartilage. Healthy cartilage is essential for the normal functioning of joints, as it reduces friction during joint movement and absorbs shock, thus protecting the bones from damage. Structurally, chondroitin is similar to glycosaminoglycans, which play a crucial role in the matrix of cartilage by providing both structure and support.
Chondroitin (Ch) works by absorbing water, maintaining the elasticity and lubrication of cartilage. When the level of chondroitin decreases, cartilage can become fragile and lose its normal function, worsening arthritis symptoms. The theory behind supplementing with Ch is to increase the concentration in the joints, improve cartilage quality, and, as a result, relieve pain and stiffness.
Video: Chondroitin Sulfate For your Joint
Clinical Research Evidence
Despite its widespread use in joint health supplements, the effectiveness of Ch remains a topic of debate in the scientific community. Numerous clinical studies have been conducted to evaluate its impact on arthritis, but the results are not entirely consistent.
Some early studies suggested that chondroitin possesses anti-inflammatory properties, reducing joint pain and improving function. For instance, a study published in 2007 found that chondroitin sulfate significantly reduced pain scores in patients with knee osteoarthritis and improved their ability to move. These findings provided theoretical support for the use of chondroitin and prompted more people to try it as a supplement.
However, more recent large-scale randomized controlled trials have produced mixed results. One such study, funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and known as the GAIT (Glucosamine/Chondroitin Arthritis Intervention Trial), found that the combination of chondroitin and glucosamine did not show significant benefits for patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis. However, in patients with more severe osteoarthritis, the combination appeared to provide some relief. This result sparked widespread discussion about the effectiveness of Ch among both academics and the general public.
Fig 1. Chondroitin sulfate powder
Why the Inconsistent Results
The varying results across different studies could be attributed to several factors. First, the effectiveness of Ch may depend on the severity of the patient’s condition. In some studies, participants may have had relatively mild arthritis, where the cartilage damage was not yet pronounced. As a result, supplementing with chondroitin sulfate may not have produced significant effects. In contrast, in studies involving patients with more advanced arthritis, where cartilage was more severely damaged, chondroitin may have had a more noticeable impact.
Second, differences in study design and methodology could also explain the inconsistent results. Factors such as the dosage of Ch, duration of use, and whether it was combined with other supplements or medications all influence the outcome. Additionally, the quality and formulation of chondroitin supplements vary between products, potentially affecting their efficacy.
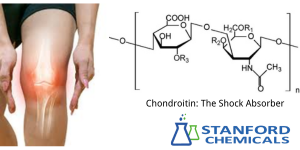
Fig 2. Chondroitin sulfate structure and the benefit of shock absorber
Considerations for Using Chondroitin
Although some studies have shown improvements in arthritis symptoms with Ch, it is essential to approach its use with caution. First, chondroitin sulfate is not a quick fix. According to clinical research, it may take at least three months of consistent use before noticeable results are observed. Therefore, individuals looking for fast pain relief may find chondroitin insufficient on its own.
Secondly, while chondroitin is generally considered safe, some mild side effects have been reported, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea. Furthermore, chondroitin may interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners. Thus, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting chondroitin sulfate, especially for individuals taking other medications.
Is Chondroitin Right for You
Chondroitin may offer some benefits for people with arthritis, particularly those with more severe symptoms. However, its effectiveness may be limited in individuals with mild osteoarthritis. If you are considering using Ch to relieve joint pain, it’s crucial to assess your specific condition, including the severity of your arthritis, your treatment goals, and the potential for side effects. A discussion with your doctor can help you make an informed decision about whether long-term use of chondroitin is appropriate for you.
Read more: Hyaluronic Acid VS. Glucosamine VS. Chondroitin: Which Is Best for Joints?
Other Ways to Manage Arthritis
In addition to chondroitin, managing arthritis often involves a multi-faceted approach. For example, regular exercise can help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength, reducing stress on the joints. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises can also effectively relieve joint pain and improve joint function.
Medications play an important role in arthritis management as well. For patients with more severe pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids may be recommended. Injections of hyaluronic acid are also a common method. In recent years, newer biological therapies and disease-modifying drugs have been developed to control the inflammatory response and progression of arthritis.
Conclusion
Chondroitin sulfate, as a natural substance, theoretically helps protect and repair joint cartilage. However, its actual effectiveness varies among individuals, especially in patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis, where the scientific evidence remains inconclusive. For patients with more advanced symptoms, Ch supplementation may offer some relief. When choosing whether to use chondroitin sulfate or other supplements, it’s important to consider your health condition, consult with a doctor, and adopt a comprehensive approach to managing arthritis to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) has developed the manufacturing and selling of Chondroitin Sulfate for over 16 years. Our products included pharmaceutical-grade and food-grade chondroitin sulfate. The sources are bovine, shark cartilage, etc.