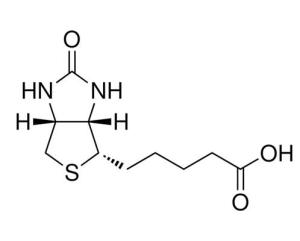
Vitamin H Description
Vitamin H, also known as biotin, is a type of B vitamin, commonly referred to as Vitamin B7. It's a water-soluble vitamin produced in the body by certain types of intestinal bacteria and obtained from food. Considered part of the B complex group of vitamins, biotin is necessary for the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids.
Health Benefits Of Vitamin H
Above normal dosing of Vitamin H has been linked to positive outcomes in a range of health conditions. These include:
- Supports Metabolism: Biotin helps in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, converting them into energy.
- Promotes Healthy Hair, Skin, and Nails: Biotin is often used to improve the health and strength of hair, skin, and nails, helping prevent hair loss and brittle nails.
- Supports Pregnancy and Fetal Development: During pregnancy, biotin is crucial for the growth and development of the fetus. It helps in regulating the metabolism and supporting healthy cell growth.
- Improves Blood Sugar Levels: Biotin may help regulate blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes, although more research is needed.
- Nervous System Health: Biotin is involved in maintaining proper function of the nervous system and may play a role in preventing cognitive decline.
Read this article to learn about the types of vitamins and their corresponding benefits: Vitamin Guide: 14 Important Vitamins for Health
Consequences of Vitamin H Deficiency
- Cradle Cap in children - a skin condition that affects the scalp (seborrheic dermatitis).
- Brittle finger and toenails.
- Poor hair condition or hair loss.
These issues can all result from a Vitamin H deficiency, so supplementing with biotin can help redress the balance.
Vitamin H Applications
- Health supplements
- Skin care products
People Also Ask
1. What is Vitamin H?
Vitamin H, or Biotin, also known as Vitamin B7, is a water-soluble B vitamin. It is an important nutrient involved in energy metabolism, skin integrity, and hair and nail development.
2. What are the main functions of Vitamin H?
It helps the body to metabolize food into energy, aids the health of skin barriers, aids hair and nail growth, and ensures proper nervous system function.
3. Whose risk is greater of developing Vitamin H deficiency?
Those who consume raw eggs in large quantities, pregnant women, long-term heavy drinkers, those with certain genetic metabolic disorders, or patients under long-term anti-epileptic treatment.
4. What are the features of Vitamin H deficiency?
Hair loss, rash (with notable emphasis in periocular, perioral, and perinasal regions), general weakness, brittle nails, conjunctivitis, or neurological abnormalities.
5. How do I naturally obtain Vitamin H?
It occurs naturally in foods such as seeds, nuts, cooked eggs, salmon, avocado, animal liver, and cauliflower.
6. Does Vitamin H really work for hair loss?
It works for hair loss caused by biotin deficiency only. If the hair loss is caused by some other factor, then supplements of biotin might not produce favorable results.
7. Are there side effects of Vitamin H?
It is very safe at therapeutic levels. Large doses can cause interference with certain laboratory tests (e.g., thyroid function tests).
8. Do pregnant women need Vitamin H supplements?
Small increased amounts are needed in pregnancy, but this can usually be attained by diet alone. Supplementation may be recommended on medical grounds if there is a risk of deficiency.
9. Can Vitamin H help the skin?
Yes, it maintains skin barrier function and moisture, particularly in dermatitis or dryness from deficiency.
10. Should one take Vitamin H supplements?
Most individuals can obtain their requirements through a varied diet. Supplementation is not usually required unless there are signs of deficiency or particular health disorders.