- Home
- Pharmaceuticals
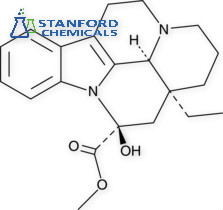
- 040-000-301 Vincamine, CAS 1617-90-9
040-000-301 Vincamine, CAS 1617-90-9
| Synonyms | Angiopac, Devincan, Equipur, Minorin |
| Source | Vincami-norL |
| Type | Indole alkaloid |
| Keywords | Metabolism, vascular, indole alkaloid, arteriosclerosis |
| Related products | Losartan Potassium, Horny Goat Weed Extract, Timclol Maleate |
- Description
Description
Description
Vincamine Description
Vincamine is an indole alkaloid found in the leaves of V. minor and C. roseus that is used as a peripheral vasodilator to increase blood flow to the brain. Vincamine contracts excised human cerebrovascular smooth muscle in vitro with an EC50 value of 30 μM and have been explored as a pharmacotherapy to treat cerebral metabolic and vascular diseases. Stanford Chemicals (SCC) provides customers with high-quality Vincamine at a very competitive price.
Vincamine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid obtained from the leaves of Vinca minor with a vasodilatory property.
Vincamine Specifications
| Product Name | Vincamine |
| CAS Registry Number | 1617-90-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C21H26N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 354.4 g/mol |
| Purity | >99% |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Package | 1kg-25kg |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | Treatment of arteriosclerosis, cerebral infarction |
Vincamine Applications
Vincamine can be used in the following fields:
- Treatment of ischemic cerebrovascular disease
- Laboratory research
Reference:
- Young, A.R., Bouloy, M., Boussard, J.F., et al. Direct vascular effects of agents used in the pharmacotherapy of cerebrovascular disease on isolated cerebral vessels. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 1(1), 117-128 (1981).
- Lim, C.C., and James, I.M. The effect of an acute infusion of vincamine and ethyl apovincaminate on cerebral blood flow in healthy volunteers. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 9(1), 100-101 (1980).
- Nowicki, J.P., MacKenzie, E.T., and Spinnewyn, B. Effects of agents used in the pharmacotherapy of cerebrovascular disease on the oxygen consumption of isolated cerebral mitochondria. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2(1), 33-40 (1982).