- Home
- Herbal Extract
- 050-000-281 Swertiamarin, CAS 17388-39-5
050-000-281 Swertiamarin, CAS 17388-39-5
| Source | Swertia L. |
| Key words | Diabetes, β cell, analgesia, promotes wound healing, skin regeneration, promotes hair growth |
| Related products | Alfa-Lipoic Acid, Biotin, β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide, Metformin (Hydrochloride) |
- Description
Description
Description of Swertiamarin
Swertiamarin is an orally bioavailable secoiridoid glycoside that has been found in E. axillare and has diverse biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, and hepatoprotective properties. Swertiamarin (50 μg/ml) inhibits nitric oxide (NO) production in IL-1β-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) isolated from rat hindpaws.
Swertiamarin (25 μg/ml) inhibits oleate-induced lipid droplet and triglyceride accumulation in HepG2 cells. It decreases liver lipid accumulation, ballooning degeneration, and TNF-α and IL-6 levels in a mouse model of fructose-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) when administered at a dose of 50 mg/kg per day. Swertiamarin (50 mg/kg per day) also decreases fasting blood glucose and serum cholesterol levels in a rat model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin.
Swertiamarin (Swertiamaroside) is a common secoiridoid found among the members of Gentianaceae with anti-inflammatory, anticancer, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic activities.
Specifications of Swertiamarin
| Product Name | Swertiamarin |
| CAS Registry Number | 17388-39-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H22O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 374.3 g/mol |
| Purity | 10-95 % |
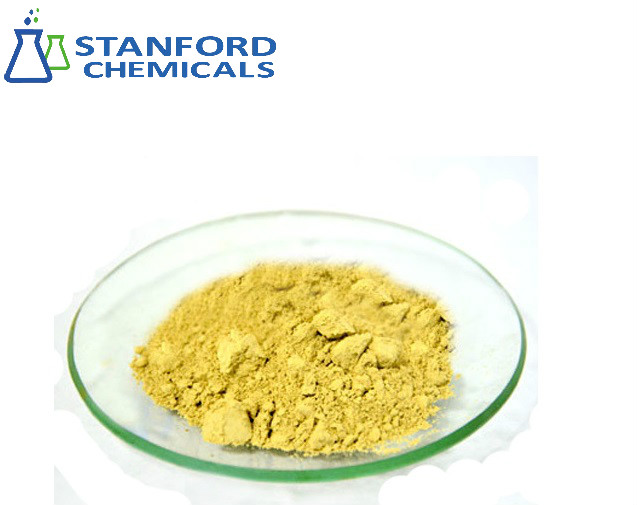
| Appearance | Pale yellow powder |
| Package | 1kg-25kg |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-diabetic activity, enhances β cell regeneration |
Benefits of Swertiamarin
- Anti-Inflammatory: Swertiamarin possesses significant anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammatory responses.
- Antioxidant: As a powerful antioxidant, Swertiamarin can combat free radical damage, aiding in the prevention of cellular aging and disease.
- Promotes Wound Healing: Research shows that Swertiamarin aids in accelerating the wound healing process, promoting tissue regeneration.
- Anti-Diabetic: Swertiamarin can help lower blood sugar levels, offering potential benefits for diabetes management.
- Hepatoprotective: It helps protect the liver, reducing liver damage and promoting liver function recovery.
Applications of Swertiamarin
– Laboratory Research:
Swertiamarin has become a subject of interest in laboratory research owing to its diverse biological activities. Studies focus on its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, and hepatoprotective properties. For instance, at a concentration of 50 μg/ml, Swertiamarin has exhibited the ability to inhibit nitric oxide (NO) production in IL-1β-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) isolated from rat hindpaws. This highlights its potential role in modulating inflammatory responses.
– Raw Materials for Hair Regeneration Products:
Beyond the laboratory, Swertiamarin contributes to the field of cosmeceuticals as raw material for hair regeneration products. Its inclusion in formulations for hair care is attributed to its purported benefits. Researchers explore its potential to stimulate hair growth, strengthen follicles, and contribute to overall hair health. As a key component in hair regeneration products, Swertiamarin represents a promising avenue in addressing various aspects of hair care and restoration.
Side Effects of Swertiamarin
While Swertiamarin offers many health benefits, it may also cause some side effects, especially at high doses or with long-term use:
- Allergic Reactions
- Gastrointestinal Discomfort
- Liver Function Abnormalities
Reference:
- Vaijanathappa, J., and Badami, S. Antiedematogenic and free radical scavenging activity of swertiamarin isolated from Enicostemma axillare. Planta Med. 75(1), 12-17 (2009).
- Saravanan, S., Islam, V.I., Thirugnanasambantham, K., et al. Swertiamarin ameliorates inflammation and osteoclastogenesis intermediates in IL-1β induced rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflamm. Res. 63(6), 451-462 (2014).
- Sonawane, R.D., Vishwakarma, S.L., Lakshmi, S., et al. Amelioration of STZ-induced type 1 diabetic nephropathy by aqueous extract of Enicostemma littorale Blume and swertiamarin in rats. Mol. Cell Biochem. 340(1-2), 1-6 (2010).
- Patel, T.P., Rawal, K., Soni, S., et al. Swertiamarin ameliorates oleic acid induced lipid accumulation and oxidative stress by attenuating gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis in hepatic steatosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 83, 785-791 (2016).
- Yang, Y., Li, J., Wei, C., et al. Amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by swertiamarin in fructose-fed mice. Phytomedicine 59, 152782 (2019).