- Home
- Pharmaceuticals
- 040-000-325 Ligustrazine Hydrochloride, CAS 76494-51-4
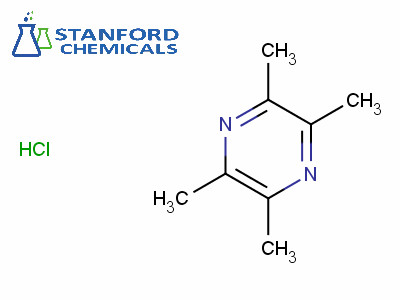
040-000-325 Ligustrazine Hydrochloride, CAS 76494-51-4
| Synonyms | 2,3,5,6-Tetramethylpyrazine hydrochloride, 2,3,5,6-Tetramethylpyrazine |
| Keywords | Cardiovascular disease, hypertension |
| Related products | Horny Goat Weed Extract, Coenzyme Q10 Powder |
- Description
Description
Description
Ligustrazine Hydrochloride Specifications
| Product Name | Ligustrazine Hydrochloride |
| CAS Registry Number | 76494-51-4 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 136.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Package | 1kg-25kg |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | Used for ischemic stroke, chest pain, swollen pain, headache, hypertension, coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, migraine, ischemic encephalopathy, etc. |
Ligustrazine Hydrochloride Description
Ligustrazine is a compound that has been found in L. wallichii and has diverse biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anticancer properties.
Ligustrazine (tetramethylpyrazine) inhibits of platelet aggregation, enhances of vessel dilation, increases cerebral blood flow and possesses neuroprotective properties. The injection solution of ligustrazine has been used especially to treat ischemic stroke, coronary heart disease, diabetic nephropathy, and knee osteoarthritis. Ligustrazine was also evaluated in clinical as a remedy for pressure sores, as a salvage agent for patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, as a treatment for bronchial asthma and vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
Ligustrazine Hydrochloride Applications
- Pharmaceutical ingredients are used for contractile stroke, chest pain, swollen pain, headache, hypertension, coronary atherosclerotic heart disease (coronary heart disease), migraine, dilated encephalopathy, etc.
Reference:
- Liao, S.-L., Kao, T.-K., Chen, W.-Y., et al. Tetramethylpyrazine reduces ischemic brain injury in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 372(1-2), 40-45 (2004).
- Wang, Y., Fu, Q., and Zhao, W. Tetramethylpyrazine inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation via downregulation of NF-κB in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Med. Rep. 8(4), 984-988 (2013).