- Home
- Pharmaceuticals
- 040-000-166 Huperzia Serrate Plant Exrtact – Huperzine A
040-000-166 Huperzia Serrate Plant Exrtact – Huperzine A
Type: Plant Extracts
CAS No: 102518-79-6
Qty in 20′ FCL: 0MT
Min. Order: 0.005KG
QC: HACCP,KOSHER,HALAL,ISO,SGS,UKAS
Packaging: Provide Neutral Packaging
Huperzia Serrate Plant Extract – Huperzine A is one of the popular food additives and ingredients in most countries.
- Description
Description
Description
Huperzine A Description
Huperzine A is a naturally occurringsesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the firmoss Huperzia serrata, and in varying quantities in other Huperzia species, including H. elmeri, H. carinat, and H. aqualupian.
HuperzineA has been investigated for its potential as a medicine for helping people with neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Huperzine A 1 Specification
| ITEM | STANDARD |
| Assay | Huperzine A NLT 1.0% |
| Appearance | Brownish yellow to brown powder |
| Odor&Taste | Characteristic |
| Loss on Drying | NMT 5.0% |
| Insoluble Ash | NMT 1.0% |
| Sieve Analysis | NLT 95% pass 80 mesh |
| Irradiation Status | Non-Irradiated |
| Heavy metals | NMT 20ppm |
| Lead (Pb) | NMT 3ppm |
| Arsenic (As) | NMT 2ppm |
| Cadmium(Cd) | NMT 0.3ppm |
| Mercury(Hg) | NMT 0.2ppm |
| BHC | NMT 0.1ppm |
| DDT | NMT 0.1ppm |
| PCNB | NMT 0.1ppm |
| Aflatoxin | NMT 5ppb |
| Total Plate Count | NMT 1,000Cfu/g |
| Total Yeast&Mold | NMT 100Cfu/g |
| E.Coli. | Negative |
| Salmonella | Negative |
| Coliforms | =<3cfu/g |
| Staphylococcus | Negative |
Huperzine A 2 Specification
| ITEM | STANDARD |
| Appearance | Off-White Fine Powder |
| Assay(HPLC) | 99.0% Min |
| Particle size | 100% pass 80 mesh |
| Loss on drying | 3% Max |
| Ash | 3% Max |
| Heavy metals | 10 ppm Max |
| As | 2 ppm Max |
| Total Plate Count | 1000cfu/g Max |
| Yeast and Mold | 100cfu/g Max |
| Salmonella | Negative |
| E.coil | Negative |
Chemical Properties:
- Molecular Formula: C₁₅H₁₈N₂O
- Molar Mass: 242.32 g/mol
- Solubility: Soluble in ethanol and methanol, slightly soluble in water.
- Chemical Structure: Huperzine A has a bicyclic alkaloid structure.
Biological Action:
- Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor: Huperzine A acts by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which breaks down acetylcholine in the brain. By preventing this breakdown, it increases acetylcholine levels, enhancing communication between nerve cells, which is critical for memory and cognitive function.
- Neuroprotective: Huperzine A also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, potentially offering protection against neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Uses and Applications:
- Cognitive Enhancement:
- Widely used in dietary supplements for its potential to enhance memory, focus, and learning capacity.
- It may improve cognitive function in individuals with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia, though more clinical studies are needed for conclusive evidence.
- Alzheimer’s Treatment: Investigated as a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s due to its acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting properties, which are similar to those of prescription drugs like donepezil.
- Neuroprotective Agent: In preclinical studies, Huperzine A has demonstrated the ability to protect brain cells from damage caused by beta-amyloid, a protein involved in Alzheimer’s pathology.
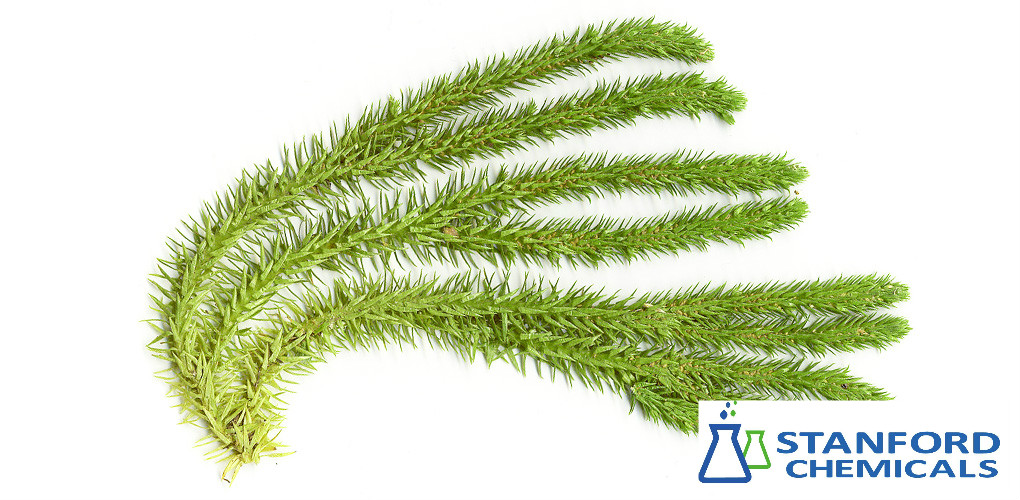
What is Huperzia serrata?
Huperzia serrata is luxuriant plants. Huperzine A extracted from a club moss (Huperzia serrata), is a sesquiterpene alkaloid and a powerful and reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) with on- and off-rates.
Huperzia serrata extract has been used for the treatment of swelling, fever and blood disorders. Huperzia serrata has demonstrated both memory enhancement in animal and clinical trials and neuroprotective effects.
Huperzia serrata has potent pharmacological effects and, particularly since long-term safety has not been determined, it should only be used with medical supervision. Huperzia serrata extract may have some effectiveness in Alzheimer’s disease and age-related memory impairment. Huperzine A has been used to treat fever and some inflammatory disorders, but there is no credible scientific evidence to support these uses.