- Home
- Pharmaceuticals
- 040-000-331 Desethyl Chloroquine, CAS 1476-52-4
040-000-331 Desethyl Chloroquine, CAS 1476-52-4
| Synonyms | N4-(7-Chloro-4-quinolinyl)-N1-ethyl-1,4-pentanediamine; Deethylchloroquine; Monodeethylchloroquine, Chloroquine Related Compound D |
| Keywords | Lupus erythematosus, COVID-19, Chloroquine |
| Related products | Chloroquine Diphosphate, Remdesivir , Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate |
- Description
Description
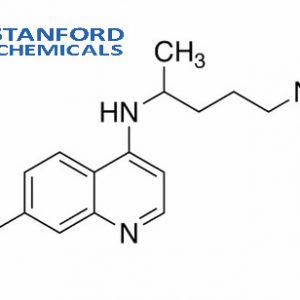
Desethyl Chloroquine Specifications
| Product Name | Desethyl Chloroquine |
| CAS Registry Number | 1476-52-4 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H22ClN3 |
| Molecular Weight | 291.82 g/mol |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | Prevention of malaria, treatment of lupus erythematosus |
Desethyl Chloroquine Description
Desethyl Chloroquine is a metabolite derived from hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine. Both hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine are well-known for their antimalarial properties and are commonly used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and other inflammatory rheumatic conditions. Recently, these drugs have gained attention for their potential effects on COVID-19, the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine impact lysosomal activity and autophagy, interact with membrane stability and modify signaling pathways and transcriptional activity, which can lead to changes in cytokine production. The precise mechanisms of their action are still being studied, and understanding their metabolism remains a significant area of interest.
Desethyl Chloroquine Synonyms
N4-(7-Chloro-4-quinolinyl)-N1-ethyl-1, 4-pentanediamine, Deethylchloroquine, Monodeethylchloroquine, NSC 13254, 7-Chloro-4-{[4-(ethylamino)-1-methylbutyl]amino}quinoline, 4-[[1-Methyl-4-((ethylamino)butyl]amino)]-7-chloroquinoline, 7-Chloro-4-(4-N-ethylamino-1-methylbutylamino)quinoline, N-Desethyl chloroquine, N-Desethylchloroquine, N4-(7-Chloro-4-quinolinyl)-N1-ethyl-1,4-pentanediamine, Monodeethylchloroquine, Monodesethylchloroquine
Desethyl Chloroquine Applications
- Used in COVID19-related research
- Used in studies to understand the metabolism and efficacy of antimalarial drugs.
- Being studied for its potential use in treating inflammatory conditions and autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
- Being studied for its ability to inhibit tumor growth and induce cancer cell apoptosis.
Reference:
- Essien, E., et al.: J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 38, 543 (1986)
- Akintonwa, A., et al.: Ther. Drug Monit., 10, 147 (1988)
- Boelaert, J., et al.: AIDS, 15, 2205 (2001)
- Basco, L., et al.: Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 47, 1391 (2003)