- Home
- Herbal Extract
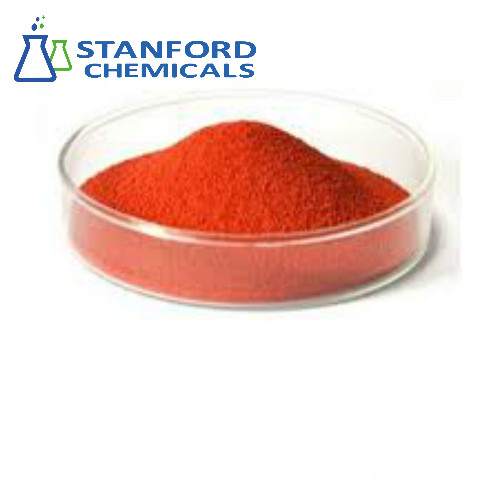
- 050-000-360 Beta-carotene (10%) (CAS: 7235-40-7)
050-000-360 Beta-carotene (10%) (CAS: 7235-40-7)
| Product Name | Beta-carotene (10%) |
| CAS No. | 7235-40-7 |
| Appearance | Red-orange powder |
| Source | Fermentation & Synthesis |
| Keywords | Beta-carotene (10%) |
| Related products | Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin C, Vitamin D3 |
| EINECS-No. | 230-636-6 |
- Description
Description
Beta-carotene (10%) Description
Beta-carotene (10%) (CAS: 7235-40-7) is a strong antioxidant and also a scavenger of singlet oxygen. It is also a provitamin A as it can be converted into retinol. In commercial cherry tomato varieties, β-carotene content reached 1.2 mg per 100 g FW. The bioaccessibility of β-carotene from raw tomatoes was reported to be about 0.1%.
Beta carotene is a yellow-orange plant pigment that gives fruits and vegetables their rich colors. Beta carotene is a carotenoid that our bodies convert into vitamin A. Beta carotene is a natural antioxidant that can be used to support healthy skin and vision.
Beta-carotene (10%) Specifications
| Product Name | Zinc L-carnosine |
| CAS Registry Number | 7235-40-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C40H56 |
| Molecular Weight | 536.9 g/mol |
| Particle Size | 40mesh |
| Assay | ≥10% |
| Loss on Drying | ≤5% |
| Heavy Metals | ≤0.001% |
| Arsenic | ≤0.0003% |
| Total Bacterial | ≤1000cfu/g |
| Mould & Yeast | ≤100cfu/g |
| Coliform | <30MPN/100g |
Beta-carotene (10%) Applications:
Studies demonstrated the photoprotective effects of β-carotene on photooxidative damage and sunburn in humans. A significant reduction in erythema formation was also noticed when β-carotene was applied on human skin or with a dietary intervention alone or in combination with α-tocopherol for 12 weeks. Low concentrations of serum β-carotene have also been associated with an increased risk of congestive heart failure and cardiac death in men.[1]
Beta-carotene is reported to be a potent antioxidant and to protect the liver against the toxic effects of various drugs and xenobiotics.
3 Studies with rats have shown that supplementation of beta carotene in diet prevented the ethanol-induced increase in the serum aminotransferases and inhibited the depletion of the antioxidant molecule GSH in the liver.
4 Additionally, in vitro studies with the hepatocytes isolated from ethanol-fed rats have also shown that beta-carotene improved cell viability and increased catalase activities and levels of glutathione.
5 Mechanistic studies performed with the hepatocytes isolated from the ethanol-fed rats have also shown that beta carotene ameliorated oxidative stress, enhanced antioxidants, and decreased the expression of CYP2E1 and apoptosis.[2]
Reference
[1] P.Padmanabhan, A.Cheema, G.Paliyath: Solanaceous Fruits Including Tomato, Eggplant, and Peppers. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384947-2.00696-6
[2] Manjeshwar ShrinathBaliga, Arnadi RamachandrayyaShivashankara, SunithaVenkatesh, Harshith P.Bhat, Princy LouisPalatty, GaneshBhandari, SureshRao: Dietary Interventions in Liver Disease Foods, Nutrients, and Dietary Supplements 2019, Pages 79-89; Chapter 7 – Phytochemicals in the Prevention of Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Revisit. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814466-4.00007-0
[3] P.Padmanabhan, A.Cheema, G.Paliyath: Solanaceous Fruits Including Tomato, Eggplant, and Peppers. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384947-2.00696-6
[4] Manjeshwar ShrinathBaliga, Arnadi RamachandrayyaShivashankara, SunithaVenkatesh, Harshith P.Bhat, Princy LouisPalatty, GaneshBhandari, SureshRao: Dietary Interventions in Liver Disease Foods, Nutrients, and Dietary Supplements 2019, Pages 79-89; Chapter 7 – Phytochemicals in the Prevention of Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Revisit. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814466-4.00007-0