What Are the Benefits of Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer
Introduction
Hyaluronic acid is widely used in reconstructive surgeries, eye surgeries, and as a cosmetic filler for wrinkles. It has excellent physical and chemical properties and is highly biocompatible. However, in the body, hyaluronic acid is quickly broken down by hyaluronidase, an enzyme, which means it does not last long and requires frequent injections to be effective.
Sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer is created by modifying hyaluronic acid with crosslinking agents. This creates a three-dimensional gel structure that is more stable. It overcomes the short duration of sodium hyaluronate in the body while maintaining good biocompatibility and effectiveness.
What Is Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer
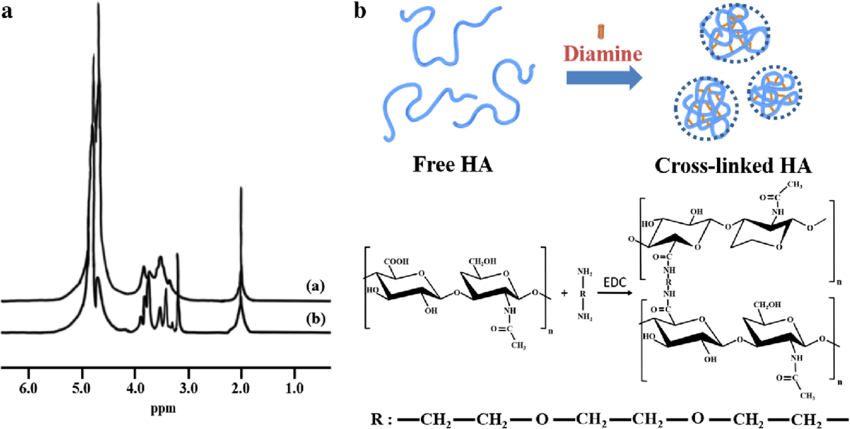
Sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer is a derivative of hyaluronic acid. It is formed through a chemical crosslinking process. In this process, molecules of hyaluronic acid or sodium hyaluronate are chemically bonded together. The reaction forms covalent bonds between the hyaluronic acid molecules, resulting in a stable three-dimensional network structure.
Fig 1. Chemical structures of Crosslinked HA and free HA[1]
–Benefits for Skincare
- Long-lasting hydration
- Improved skin barrier function
- Skin smoothing
- Reduced appearance of fine lines
–Advantages: Stability of the Crosslinked Structure
The crosslinked three-dimensional network of sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer forms a stable moisturizing film on the skin’s surface. This film not only retains moisture and provides long-lasting hydration but also creates a physical barrier on the skin. This barrier helps protect the skin from external irritants and prevents moisture loss. Because of the stability of the crosslinked structure, sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer offers more durable and effective moisturizing properties in skincare products.
–Synonyms
Sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer may have different names or similar terms in cosmetic ingredient lists. These include:
- Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid: This name emphasizes its nature as a crosslinked hyaluronic acid polymer.
- Hyaluronic Acid Crosspolymer: Another variant that describes its crosslinked structure.
- Hyaluronan Crosspolymer: Sometimes used to refer to the crosslinked polymer form of the sodium salt of hyaluronic acid.
Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer vs. Hyaluronic Acid: Different Benefits for Skincare
Both sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer and hyaluronic acid provide moisturizing and anti-aging benefits, but they have significant differences in function and application.
Fig 2. Crosslinked HA benefits
1. Molecular Size and Penetration Ability
- Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer: Due to its crosslinked structure, it has a larger molecular weight. It mainly stays on the surface of the skin and does not easily penetrate deeper layers. It forms a protective film that locks in moisture and provides continuous hydration on the skin’s surface.
- Hyaluronic Acid: Available in a range of molecular weights, from large to small. Smaller molecules can penetrate deeper into the skin, providing deep hydration, while larger molecules stay on the surface, offering immediate hydration.
2. Moisturizing Effect
- Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer: Primarily provides long-lasting surface hydration. Its crosslinked structure allows it to form a durable moisturizing film on the skin, which helps prevent water loss.
- Hyaluronic Acid: Has a strong water-binding capacity, capable of holding many times its weight in water. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid provides surface hydration, while low molecular weight hyaluronic acid penetrates deeper for more intensive hydration.
3. Stability
- Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer: Its crosslinked structure is stable and not easily broken down by enzymes in the skin. This allows it to remain on the skin longer, providing extended moisturizing benefits.
- Hyaluronic Acid: Although natural, it is more easily degraded by hyaluronidase in the skin, making its moisturizing effect shorter-lasting.
4. Skin Barrier Function
- Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer: The protective film it forms on the skin helps strengthen the skin barrier, prevents moisture loss, and protects against environmental pollutants.
- Hyaluronic Acid: Mainly used for hydration, it does not provide a physical barrier but maintains skin health by drawing moisture into the skin.
5. Application Scenarios
- Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer: Suitable for products requiring long-lasting hydration and enhanced skin barrier function, such as moisturizers, night masks, and anti-aging products.
- Hyaluronic Acid: Widely used in various skincare products, including hydrating serums, toners, masks, and eye creams. It is ideal for quick hydration and deep moisturizing needs.
Table 1. Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer vs. Hyaluronic Acid
| Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer | Hyaluronic Acid | |
| Molecular Size | Larger molecules | Various sizes |
| Penetration | stays on surface, forms film | small ones penetrate deeper |
| Moisturizing Effect | Long-lasting surface hydration | Strong hydration, deeper with small molecules |
| Stability | Stable, not easily broken down | Natural, breaks down faster |
| Skin Barrier Function | Strengthens barrier, protects skin | Hydrates, no barrier |
| Application Scenarios | Moisturizers, night masks, anti-aging products | Serums, toners, masks, eye creams |
Table 1 summarizes the above content and compares the differences between the two in terms of molecular weight, Penetration, moisturizing effect, stability, skin care barrier effect, and application.
Where to Buy Sodium Hyaluronate Crosspolymer
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a premium supplier specializing in sodium hyaluronate powder. Our product range includes:
- Cosmetic Grade Sodium Hyaluronate
- Medical Grade Sodium Hyaluronate
- Injection Grade Sodium Hyaluronate
- Cross-linked HA Gel Hyaluronic Acid
- Hymagic 4D Hyaluronic Acid
- Hyacross Hyaluronic Acid Elastomer
- Super Active Hyaluronic Acid
Our sodium hyaluronate powder is Ecocert certified and produced under strict ISO 9001 and GMP standards. All products are fermentation-based, non-animal origin, non-GMO, and carry no BSE/TSE risk.
Conclusion
Sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer and hyaluronic acid both offer unique benefits for skincare. Choosing the right ingredient depends on individual skin needs. For long-lasting hydration and barrier protection, sodium hyaluronate crosspolymer is the better choice. For immediate and deep hydration, hyaluronic acid is more suitable. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the best skincare products for your routine.
[1] Kim, Dae-Sung & Choi, Jun-Tae & Kim, Cheong & Shin, Yu-Ra & Park, Pil-gu & Kim, Hyemi & Lee, Jae Myun & Park, Jung-Hwan. (2020). Microneedle Array Patch (MAP) Consisting of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles for Processability and Sustained Release. Pharmaceutical Research. 37. 10.1007/s11095-020-2768-3.