Something you need to know about Coenzyme Q10
Introduction
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), also known as ubiquinone, is a naturally occurring compound that plays a critical role in the body’s energy production and acts as a powerful antioxidant. Given its pivotal functions, it’s no surprise that CoQ10 supplementation has garnered attention for its potential health benefits.
However, like any supplement, CoQ10’s interaction with other nutrients, particularly certain vitamins, warrants careful consideration. This article delves into the essentials of CoQ10, its uses, and its crucial interactions with vitamins, offering a comprehensive guide to understanding this vital compound.
Understanding Coenzyme Q10
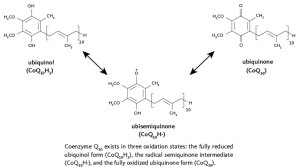
CoQ10 is found in every cell of the body, concentrated in organs that require the most energy – such as the heart, liver, kidneys, and muscles. It exists in two main forms: ubiquinone (oxidized form) and ubiquinol (reduced form), with the latter being the active antioxidant form. The body naturally produces CoQ10, but its levels decline with age and in certain disease states, prompting interest in CoQ10 supplementation.
The Multifaceted Uses of CoQ10
–Heart Health
CoQ10 is renowned for its cardiovascular benefits. It’s been shown to improve symptoms of congestive heart failure and may help lower blood pressure. Additionally, CoQ10 can reduce the muscle pain and weakness associated with statin use, a common side effect due to statins’ tendency to lower CoQ10 levels in the body.
–Neuroprotection and Aging
Research suggests CoQ10’s antioxidant properties may protect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s by mitigating oxidative damage and supporting mitochondrial function.
–Energy and Exercise Performance
CoQ10’s role in energy production has implications for exercise performance and energy levels. Supplementation may increase power during exercise and reduce fatigue, enhancing overall physical performance.
–Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Emerging evidence indicates CoQ10 may improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels, making it a potential adjunctive therapy for managing diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Nutrient Interactions with CoQ10
While CoQ10 can be a valuable addition to one’s supplement regimen, it’s crucial to be aware of its interactions with other vitamins and nutrients.
1. Vitamin E
CoQ10 and vitamin E are both lipid-soluble antioxidants, and they work synergistically to combat oxidative stress in the body. However, they can compete for absorption and utilization in the body. Excessive supplementation of one can potentially deplete the other.
It’s generally recommended to balance these nutrients and consider taking them at different times of the day to optimize their benefits.
2. Vitamin K
The interaction between CoQ10 and vitamin K is not inherently negative, but caution is advised for individuals on blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin, which works by inhibiting vitamin K. Since CoQ10 structurally resembles vitamin K, high doses of CoQ10 could potentially decrease the effectiveness of warfarin, leading to an increased risk of blood clots.
It’s important for individuals on blood thinners to consult healthcare providers before starting CoQ10 supplementation.
Cautions and Considerations
While Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is celebrated for its myriad health benefits, ranging from enhancing heart health to boosting energy levels, it’s crucial to approach its supplementation with awareness of potential cautions and considerations. Understanding these factors can ensure that you harness CoQ10’s benefits while minimizing any risks.
–Interactions with Medications
- Blood Thinners
CoQ10’s structural similarity to vitamin K can interfere with blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin, potentially reducing their efficacy and increasing the risk of clot formation. If you’re on a blood thinner, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting CoQ10 supplementation.
- Chemotherapy Drugs
There is some concern that CoQ10’s antioxidant properties might reduce the effectiveness of certain chemotherapy drugs. Cancer patients should discuss CoQ10 supplementation with their oncologist to avoid potential interactions.
- Blood Pressure Medications
CoQ10 may enhance the effects of medications designed to lower blood pressure, leading to hypotension. Monitoring blood pressure and adjusting medications as necessary can mitigate this risk.
–Side Effects and Dosage Considerations
While CoQ10 is generally well-tolerated, exceeding recommended doses can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, diarrhea, and appetite loss. Rarely, it may cause allergic skin rashes. To avoid these side effects, adhere to the dosage guidelines provided by your healthcare professional or the supplement manufacturer.
–Age and Health Status
The body’s ability to synthesize CoQ10 decreases with age, potentially increasing the elderly’s need for supplementation. However, older adults often take medications for chronic conditions, heightening the importance of monitoring for drug-nutrient interactions. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing conditions should consult healthcare providers to ensure CoQ10’s suitability for their specific health profile.
–Dietary and Lifestyle Factors
CoQ10’s absorption can be influenced by dietary and lifestyle factors. Being fat-soluble, its absorption improves when taken with meals containing fats. Certain health conditions and lifestyle choices, such as smoking, can also impact CoQ10 levels in the body, affecting supplementation needs.
Therefore, by taking a measured, informed approach and consulting with healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively integrate CoQ10 into their health regimen, optimizing its benefits while ensuring safety and compatibility with their overall health strategy.
Conclusions
In a word, CoQ10 stands out for its essential role in energy production and antioxidant protection. Its diverse health benefits, from enhancing heart health and physical performance to offering neuroprotective effects, make it a significant supplement for many.
Yet, understanding its interactions with other nutrients, especially vitamins E and K, is crucial for harnessing CoQ10’s full potential without unintended consequences. As with any supplement, consulting with a healthcare professional to tailor CoQ10 use to individual health profiles and dietary patterns is advisable, ensuring optimal health outcomes and nutritional balance.
Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) is recognized as a reliable supplier of Coenzyme Q10, catering to a wide range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, and cosmetics. Send us an inquiry if you are interested.
Reference:
[1] The Linus Pauling Institute’s Micronutrient Information Center (MIC) (2024, April 11). Coenzyme Q10. Oregon State University. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/coenzyme-Q10
