- Home
- Foods and Nutraceuticals
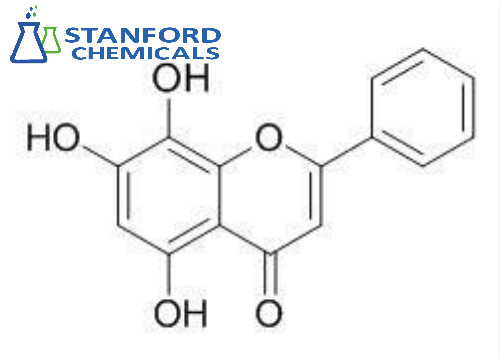
- 030-000-363 Norwogonin (CAS: 4443-09-8)
030-000-363 Norwogonin (CAS: 4443-09-8)
| Product Name | Norwogonin |
| CAS No. | 4443-09-8 |
| Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Type | Flavone |
| Keywords | Norwogonin, 5,7,8-trihydroxyflavone (5,7,8-THF) |
| Related products | Medical Grade Sodium Hyaluronate, Chondroitin Sulfate, Dihydromyricetin, Herbal Extract |
| Synonyms | 5,7,8-trihydroxyflavone (5,7,8-THF) |
- Description
Description
Norwogonin (CAS: 4443-09-8) Description
Norwogonin (CAS: 4443-09-8), also known as 5,7,8-trihydroxy flavone (5,7,8-THF), is a flavone, a naturally occurring flavonoid-like chemical compound that is found in Scutellaria baicalensis (Baikal skullcap). It has been found to act as an agonist of the TrkB, the main signaling receptor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and appears to possess roughly the same activity in this regard as that of the closely related but more well-known 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF).
Norwogonin is a natural flavone with three phenolic hydroxyl groups in skeletal structure and has excellent antioxidant activity.
Norwogonin (CAS: 4443-09-8) Specifications
| Product Name | Norwogonin |
| CAS Registry Number | 4443-09-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 270.24 g/mol |
| Assay | ≥98% |
| Storage | -20°C, ≥2 years |
| Shipping | Room Temperature in the Continental US |
Norwogonin (CAS: 4443-09-8) Applications
Norwogonin (CAS: 4443-09-8) had excellent antioxidant activity, suggesting that C8-OH was the prominent antioxidant active group for them. More importantly, the findings indicated that norwogonin and isowogonin afforded outstanding antioxidant capacity and might be promising candidates as dietary natural products in the treatment of oxidative-related diseases.[1]
It has been shown that norwogonin causes a substantial reduction in the viability of the human colorectal carcinoma cells in a dose-dependent manner, exhibiting an IC50 of 15.5 µM in cancer cells and IC50 of 90 µM in normal cell lines. The AO/EB staining assay showed that norwogonin suppresses the viability of cancer cells via induction of apoptotic cell death which was associated with an increase in Bax and a decrease in Bcl-2 levels. Comet assay results also confirmed that norwogonin induces apoptosis. Norwogonin also led to the induction of autophagy along with triggering G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. In conclusion, the current study shows that norwogonin has the potential to inhibit in vitro colorectal cancer cell growth by triggering apoptosis, autophagy, and cell cycle arrest and as such could be developed as a possible anticancer agent.[2]
Reference
Qiushan Zhang, Qiushan Zhang, Qiushan Zhang, Lei He, Huiping Ma, Linlin Jing: The Role of C-8 OH on the Antioxidant Activity of Norwogonin and Isowogonin. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X20924887
Zhang Wang, Qinqin Zhang, Ling Zhou, Gao Liu, Quanfeng Wu, Changwang Chen: Norwogonin flavone suppresses the growth of human colon cancer cells via mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, autophagy induction, and triggering G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. JBUON 2020; 25(3): 1449-1454
[1] Qiushan Zhang, Qiushan Zhang, Qiushan Zhang, Lei He, Huiping Ma, Linlin Jing: The Role of C-8 OH on the Antioxidant Activity of Norwogonin and Isowogonin. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X20924887
[2] Zhang Wang, Qinqin Zhang, Ling Zhou, Gao Liu, Quanfeng Wu, Changwang Chen: Norwogonin flavone suppresses the growth of human colon cancer cells via mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, autophagy induction, and triggering G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. JBUON 2020; 25(3): 1449-1454