- Home
- Cosmetics & Personal Care
- 070-000-345 Kojic Acid, CAS 501-30-4
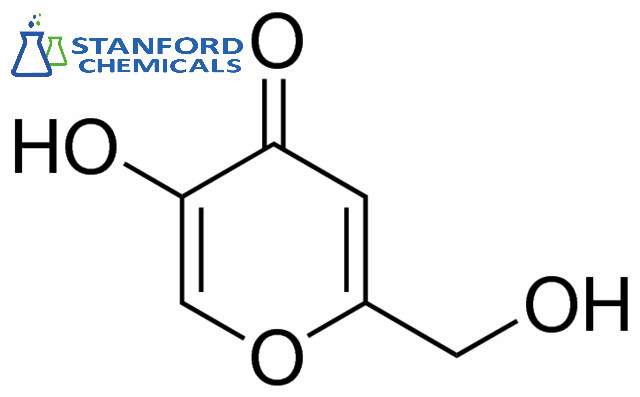
070-000-345 Kojic Acid, CAS 501-30-4
| Synonyms | 5-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4H-pyran-4-one |
| Source | fermentation |
| Keywords | Whitening, spot solution |
| Related products | Licochalcone A, Biotin, Stearyl Glycyrrhetinate, Monoammonium Glycyrrhizinate |
- Description
Description
Kojic Acid Specifications
| Product Name | Kojic Acid |
| CAS Registry Number | 501-30-4 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 142.11 g/mol |
| Purity | 99 % |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Package | 1kg-25kg |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | Whitening, spot solution, inhibition of tyrosinase activity |
Kojic Acid Description
Since it was discovered, kojic acid was first used in food, medicine, agriculture, and other fields. In the food field, it can be used as a food additive, which plays a role in preservation, antiseptic, and anti-oxidation. Later, some research institutions found that “Kojic acid” has a good whitening effect and can lighten stains. After this application was discovered, “Kojic acid” began to be used as a skin whitening agent and was widely used in whitening and lightening products.
Kojic acid is a chemical derived from mushrooms, but it can also be created during the sake brewing process from fermented rice.
Because of its ability to really penetrate the layers of your skin and stop the production of melanin, kojic acid is usually sought out as a spot-fading treatment and is often considered a less-aggressive answer to hydroquinone.
Kojic Acid Application
- As an ingredient in whitening personal care products
Reference:
- Lee, Y.S., Park, J.H., Kim, M.H., et al. Synthesis of tyrosinase inhibitory kojic acid derivative. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim) 339(3), 111-114 (2006).
- Rodrigues, A.P., Farias, L.H., Carvalho, A.S., et al. A novel function for kojic acid, a secondary metabolite from Aspergillus fungi, as antileishmanial agent. PLoS One 9(3), e91259 (2014).
- Wang, K., Liu, C., Di, C.-J., et al. Kojic acid protects C57BL/6 mice from gamma-irradiation induced damage. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 15(1), 291-297 (2014).