- Home
- Pharmaceuticals
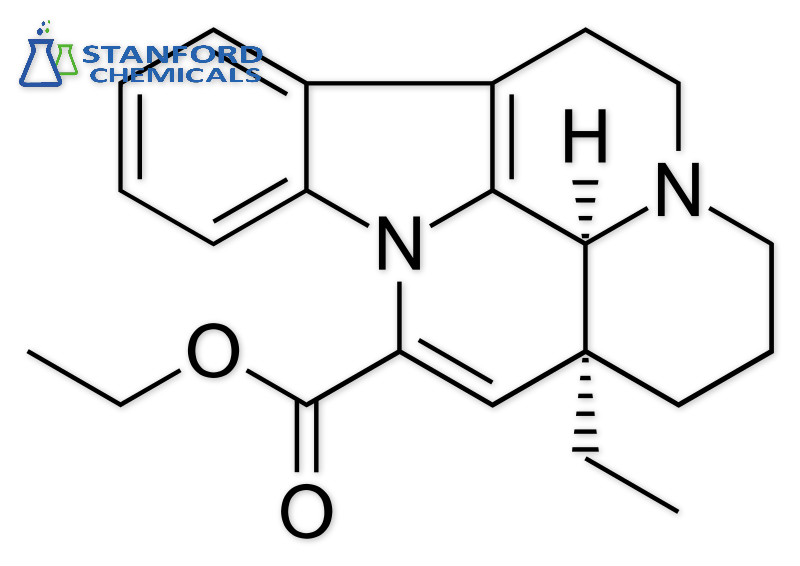
- 040-000-302 Vinpocetine, CAS 42971-09-5
040-000-302 Vinpocetine, CAS 42971-09-5
| Synonyms | Apovincaminic Acid ethyl ester, (3α,16α)-eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester |
| Type | Derivative of vinca alkaloid vincamine |
| Source | Voacanga Africana/ vinca minor |
| Keywords | Cerebrovascular, dopamine |
| Related products | Losartan Potassium, Horny Goat Weed Extract, Timclol Maleate |
- Description
Description
Description
Vinpocetine Specifications
| Product Name | Vinpocetine |
| CAS Registry Number | 42971-09-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C22H26N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 350.5 g/mol |
| Purity | >99 % |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Package | 1kg-25kg |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | Treatment of cerebrovascular |
Vinpocetine Description
Vinpocetine is a semi-synthetic alkaloid commonly used as an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 1 (PDE1), blocking the hydrolysis of both cAMP and cGMP. In addition to its use as a selective PDE1 inhibitor in basic research, vinpocetine has diverse cerebral and neurological effects in vivo. Vinpocetine also directly inhibits the kinase activity of IKKβ and blocks TNF-α- and LPS-mediated activation of NF-κB in cells and in vivo. Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) provides customers with high-quality vinpocetine at a very competitive price.
Vinpocetine is a partially synthesized supplement created from vincamine, which is derived from the seeds of the periwinkle plant.
Vinpocetine Applications
Vinpocetine can be used in the following fields:
- Laboratory research
- Treatment of cerebrovascular
Reference:
- Jeon, K.I., Xu, X., Aizawa, T., et al. Vinpocetine inhibits NF-κB-dependent inflammation via an IKK-dependent but PDE-independent mechanism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107(21), 9795-9800 (2016)
- Medina, A.E. Therapeutic utility of phosphodiesterase type I inhibitors in neurological conditions. Front.Neurosci. 5(21), (2011).