- Home
- Pharmaceuticals
- 040-000-296 Ritonavir, CAS 155213-67-5
040-000-296 Ritonavir, CAS 155213-67-5
| Synonym | Norvir |
| Type | Antibiotics, protease, tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| Keywords | COVID-19, HIV, antiviral, AIDS, SARS-CoV-2 |
| Related products | Piperaquine, Chloroquine Diphosphate, Artemisinin, Acrichin Dihydrochloride |
- Description
Description
Ritonavir Specifications
| Product Name | Ritonavir |
| CAS Registry Number | 155213-67-5 |
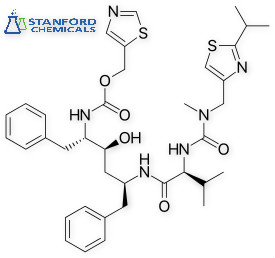
| Molecular Formula | C37H48N6O5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 720.946 g/mol |
| Purity | 98% |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Package | 1kg-25kg |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Functions | Antiviral, therapy for HIV-1, potential inhibitor of COVID-19 |
Ritonavir Description
Ritonavir is an HIV protease inhibitor that interferes with the reproductive cycle of HIV. The mechanism of action of the anti-HIV drug lopinavir and ritonavir is to block the enzymes required for virus replication. It is often used in combination with other antiretrovirals and serves as both a protease inhibitor and a pharmacokinetic enhancer. Lopinavir/ritonavir have been shown to reduce coronavirus levels that cause SARS and MERS in animal studies.
Ritonavir is an HIV protease inhibitor that interferes with the reproductive cycle of HIV.
ritonavir
Ritonavir Solubility / Properties
Ritonavir is poorly soluble in water, with solubility less than 1 mg/mL at physiological pH. This poor solubility can impact its bioavailability and absorption in the body, necessitating the use of formulations that enhance its solubility for effective therapeutic use.
Ritonavir Half-Life
The half-life of ritonavir is approximately 3 to 5 hours. However, due to its role as a CYP3A4 inhibitor, the half-lives of other drugs metabolized by this enzyme can be significantly prolonged when co-administered with ritonavir. This pharmacokinetic interaction is a key reason ritonavir is used as a booster for other protease inhibitors.
Ritonavir Applications
Ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infected patients (adults and children of 2 years of age and older).
Ritonavir is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4). This inhibition allows ritonavir to boost the levels of co-administered drugs that are substrates of CYP3A4, particularly other protease inhibitors used in the treatment of HIV.
Reference:
- L. Morissette; S. Soukasene; D. Levinson; M. J. Cima; O. Almarsson (2003). “Elucidation of crystal form diversity of the HIV protease inhibitor ritonavir by high-throughput crystallization”
- Hsieh, Yi-Ling; Ilevbare, Grace A.; Van Eerdenbrugh, Bernard; Box, Karl J.; Sanchez-Felix, Manuel Vincente; Taylor, Lynne S. (2012-05-12). “pH-Induced Precipitation Behavior of Weakly Basic Compounds: Determination of Extent and Duration of Supersaturation Using Potentiometric Titration and Correlation to Solid State Properties”. Pharmaceutical Research. 29 (10): 2738–2753.
- Nieminen, Tuija H.; Hagelberg, Nora M.; Saari, Teijo I.; Neuvonen, Mikko; Neuvonen, Pertti J.; Laine, Kari; Olkkola, Klaus T. (2010). “Oxycodone concentrations are greatly increased by the concomitant use of ritonavir or lopinavir/ritonavir”. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 66 (10): 977–985.