- Home
- Foods and Nutraceuticals
- Glucosamine, CAS 3416-24-8
Glucosamine, CAS 3416-24-8
Glucosamine is a precursor of multiple cartilage constituents, which is extracted from chitin. Glucosamine is commercially sold in the form of glucosamine sulfate 2KCl/HCl.
- Description
Description
Glucosamine Description
Glucosamine is a precursor of multiple cartilage constituents, which is extracted from chitin. Glucosamine is commercially sold in the form of glucosamine sulfate 2KCl/HCl.
Strong scientific evidence supports the use of glucosamine sulfate for treatments of mild to moderate osteoarthritis of the knee. Glucosamine often is taken along with chondroitin sulfate for a better effect.
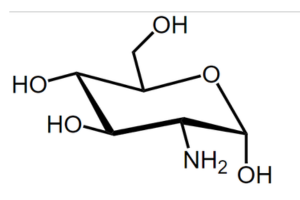
Glucosamine Structure
Glucosamine Properties
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H13NO5 |
| Molar mass | 179.17 g·mol⁻¹ |
| Melting point | 150 °C (423 K) |
How does Glucosamine work?
Glucosamine helps rebuild and repair damaged cartilage. In addition, glucosamine may have mild anti-inflammatory effects, helping to reduce joint swelling and discomfort.
Glucosamine Benefits /Applications
Relieve osteoarthritis: Some research suggests that glucosamine salts can provide some relief for people with osteoarthritis of the knee. It may also help slow knee joint degeneration associated with osteoarthritis.
Relieve rheumatoid arthritis: Early research suggests that glucosamine may reduce pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
Safety and Side Effects of Glucosamine
The typical dose of glucosamine is 1,500-3,000 mg per day. Glucosamine sulfate appears to be safe as long as it is taken in moderation. General side effects of glucosamine may include:
- Nausea
- Heartburn
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Skin reactions
- Headache
- May increase eye pressure
- May aggravate asthma
In addition, because glucosamine products may be derived from shellfish, they may cause allergic reactions in people with shellfish allergies.
Related Articles:
Chondroitin Sulfate VS Glucosamine
What is the Difference Between Glucosamine Sulfate And Chondroitin Sulfate?