Summary: Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies
Artemisinin and its derivatives (such as artesunate and dihydroartemisinin) have shown remarkable potential not only in anti-malarial treatment but also in the fields of cancer, viral infections, and autoimmune diseases. Combination therapy can enhance efficacy, reduce resistance, and lower the side effects associated with monotherapy.
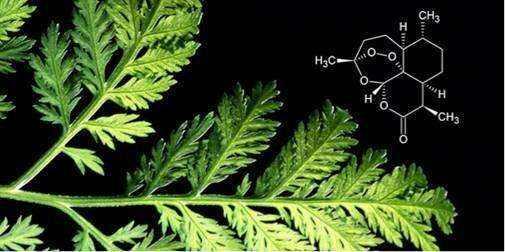
Fig 1. Artemisinin source and structure
Advantages of Artemisinin Combination Therapy
Artemisinin combination therapy enhances efficacy, reduces recurrence, delays resistance, and minimizes side effects across various treatments.
–Improving Efficacy
Artemisinin acts quickly but has a very short half-life. Using long-acting drugs like piperaquine for malaria, along with treatments like cisplatin or PD-1 antibodies, can improve results. This approach targets pathogens or tumor cells more effectively.
–Reducing Recurrence
Using other drugs, like mefloquine or ribavirin, lowers the risk of drug resistance. This happens because these drugs attack pathogens or viruses in different ways. As a result, the chances of survival for these harmful agents decrease.
–Reducing Drug Resistance
Combination with other drugs (e.g., mefloquine or ribavirin) decreases the risk of drug resistance by attacking pathogens or viruses through multiple mechanisms, hence diminishing their chances of survival.
–Lowering Side Effects
Combining therapies helps reduce the dose of harmful drugs. For example, it can lower steroid use in autoimmune diseases. This decreases side effects while keeping the treatment effective.
Anti-Malarial Combination Therapy
In the anti-malarial field, combination therapy is currently the main strategy for treating malaria, particularly to counteract resistance to Plasmodium parasites. Artemisinin-based Combination Therapies (ACTs) have been recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) as the first-line treatment for malaria.
Artemisinin and its derivatives can quickly lower the number of parasites in the body. Combination therapies also help reduce the risk of resistance to one drug.
List of artemisinin combination therapy for malarial:
| Combination Drug | Effect |
| Chloroquine | Initially combined for malaria treatment, but its use decreased due to chloroquine resistance. |
| Mefloquine | Combined for the treatment of resistant falciparum malaria. |
| Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP) | Combined to improve efficacy against falciparum malaria. |
| Piperaquine | Artemisinin-piperaquine combination therapy (ACT) is recommended by WHO as a standard treatment for malaria. |
| Amodiaquine | Can be combined for the treatment of pediatric malaria. |
Anti-Cancer Combination Therapy
Artemisinin and its derivatives have recently been found to possess anti-cancer properties. Based on iron-dependent cytotoxicity, artemisinin selectively targets cancer cells, inducing apoptosis. Studies have shown that artemisinin exhibits inhibitory effects on breast cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, colorectal cancer, leukemia, and ovarian cancer. [1]Combining artemisinin with other drugs can enhance efficacy and improve treatment outcomes.
List of combination therapies for cancers:
| Combination Drug | Effect |
| Iron supplements (e.g., ferrous sulfate) | Increase intracellular iron concentration in cancer cells, enhancing artemisinin’s selective cytotoxic effect. |
| Cisplatin | Combined for the treatment of ovarian and lung cancers. |
| Docetaxel | Improves treatment efficacy against breast cancer. |
| Immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., PD-1 antibodies) | Combined to enhance immune response. |
| Vitamin C | Combined to promote oxidative stress and free radical generation, enhancing anti-cancer effects. |
Anti-Viral Combination Therapy
Artemisinin exhibits multiple mechanisms of action, including anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, and immune-regulating effects. Artemisinin and its derivatives can block SARS-CoV-2. They may stop the virus from entering host cells or reduce its replication[2] Some clinical trials have evaluated the effects of artemisinin in combination with other drugs.
Anti-Viral combination therapy list:
| Combination Drug | Effect |
| Lopinavir | Artemisinin combined with these anti-HIV drugs has shown synergistic effects in studies on SARS-CoV-2 |
| Ribavirin | Help suppress RNA virus infections |
| Interferon | Combined to enhance host immune responses and inhibit viral replication |
Combination Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
T cells and B cells are important for the immune system. When they are activated incorrectly, it can lead to autoimmune diseases.
Artemisinin-based drugs can affect how T cells and B cells work. They can stop these cells from activating and reduce the release of inflammatory cytokines. This helps to ease autoimmune diseases.
Combining artemisinin with other drugs can improve efficacy and reduce adverse effects, particularly in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and multiple sclerosis (MS).
Combination therapies for autoimmune diseases:
| Combination Drug | Effect |
| Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) | Combined to improve arthritis symptoms and relieve joint swelling and morning stiffness |
| Immunosuppressants (e.g., cyclophosphamide) | May regulate immune function and improve SLE symptoms |
| Interferon-β | Reduces relapse rates and alleviates inflammatory damage in MS |
| Sulfasalazine | Combined to improve symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease. |
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is an excellent supplier of Sodium Hyaluronate Powder and various herbal extracts. We offer various molecular-weight sodium hyaluronate powder, artemisinin, dihydromyricetin, and chondroitin sulfate. For more information on these materials, please check out our home page.
[1] Anna Maria Posadino, Roberta Giordo, Gianfranco Pintus, Medicinal and mechanistic overview of artemisinin in the treatment of human diseases, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 163, 2023, 114866, ISSN 0753-3322, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114866.
[2] Beyraghdar Kashkooli, A., Babaei, A., Rezaei, A., & R., A. (2022). Artemisinins in Combating Viral Infections Like SARS-CoV-2, Inflammation and Cancers and Options to Meet Increased Global Demand. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 780257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.780257