Sodium Hyaluronate: Uses, Molecular Weight, Production and Derivatives
When sodium hyaluronate is mentioned, many people might first think of the “hydrating ingredient” in skincare products, but its story goes far beyond that. As a powerful biological molecule, it plays a significant role in beauty, medicine, and health care.
Multiple Functions of Sodium Hyaluronate
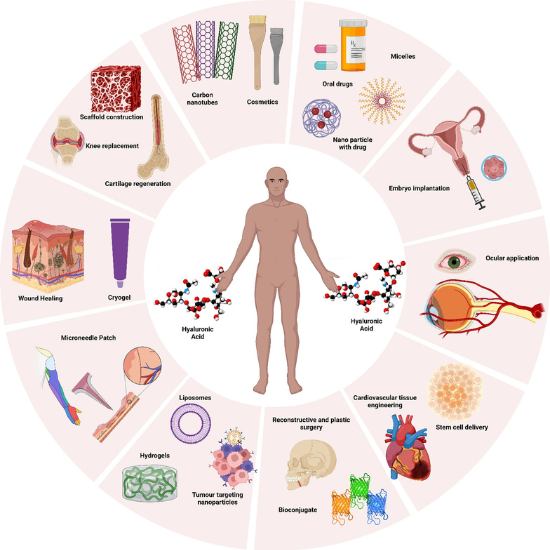
From skincare to medicine, joint care to genetic engineering, sodium hyaluronate has become an indispensable part of modern technology and daily life.
Fig 1. Wide range of uses for hyaluronic acid
–A Multifunctional Skincare Ingredient
Sodium hyaluronate is a star in skincare products. It boasts excellent moisturizing properties, repairs the skin barrier, and fights aging. It quickly increases the skin’s water content, restoring its radiance. Whether it’s a luxury serum or an affordable mask, you’re likely to find its presence.
Read more: Hyaluronic Acid vs Glycerin: Which is More Hydrating
–A Star Ingredient in the Beauty Industry
It is not only a key ingredient in skincare but also a celebrity in the beauty field. From injectable fillers and skin tightening to restoring elasticity, sodium hyaluronate plays a crucial role.
— A Key Component of Artificial Tears
For modern individuals who spend extended periods staring at screens, dry eye syndrome has become a common issue. Sodium hyaluronate, with its excellent lubricating and moisturizing properties, is widely used in artificial tears, effectively alleviating eye discomfort and fatigue.
Read more: From Surgery to Daily Care: The Versatile Role of Sodium Hyaluronate in Eye Health
— A Miracle Ingredient for Joint Pain Relief
Joint problems are often caused by the loss of hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid. Sodium hyaluronate is used in joint injection solutions to provide lubrication, reduce friction and pain, and restore mobility for osteoarthritis patients.
— Significant Applications in Medicine
In surgeries, sodium hyaluronate serves as a tissue filler or drug carrier, accelerating tissue healing and reducing inflammation. Additionally, it is used in wound repair and oral care, demonstrating extraordinary medical value.
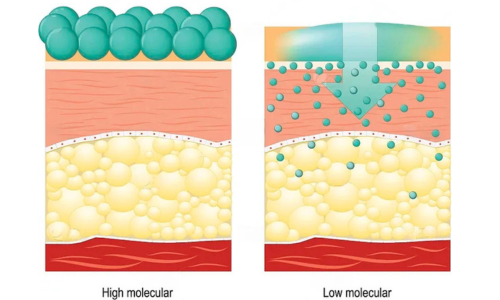
How Molecular Weight Affects Sodium Hyaluronate Uses
The molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate determines its characteristics in absorption, penetration, lubrication, and repair, making it a crucial reference for its specific applications.
Fig 2. HA with different molecular weights has different permeability
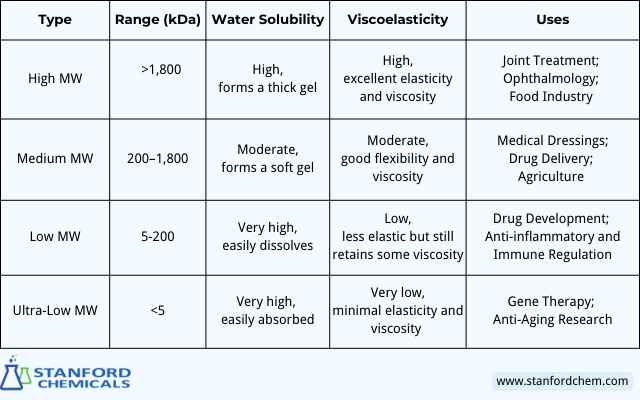
–High Molecular Weight HA: Preferred for Barrier and Lubrication
High molecular weight (>1,800 kDa) sodium hyaluronate tends to remain on the surface, forming a viscoelastic film.
- Joint Treatment: In osteoarthritis therapy, it enhances the viscoelasticity of joint fluid, reduces friction, and alleviates pain.
- Ophthalmology: Its lubricating properties protect the cornea and alleviate discomfort in dry eyes, particularly for contact lens wearers.
- Food Industry: Used as a food additive to improve oral and esophageal lubrication, aiding those with swallowing difficulties.
— Medium Molecular Weight HA: Balanced Properties for Broad Applications
Medium molecular weight (200–1,800 kDa) sodium hyaluronate offers a balance of surface action and penetration.
- Medical Dressings: Exhibits excellent tissue repair properties for burns and wounds, covering surfaces while promoting regeneration.
- Drug Delivery: Used as a matrix material for drug delivery systems, enabling slow drug release and improved bioavailability.
— Low Molecular Weight HA: Core for Penetration and Repair
Low molecular weight (5-200 kDa) sodium hyaluronate has excellent penetration properties, reaching deep into tissues or cells.
Aesthetic Treatments: Used for deep tissue filling in injections, such as correcting depressions or scar repair.
- Drug Development: Its penetration performance makes it an effective drug carrier for cancer and immune regulation treatments.
- Anti-inflammatory and Immune Regulation: It modulates inflammatory responses, aiding in pathological inflammation suppression in immunological research and therapies.
— Ultra-Low Molecular Weight HA: Exploring Frontier Functions
Ultra-low molecular weight (<5 kDa) sodium hyaluronate has drawn attention in modern medicine and biotechnology.
- Gene Therapy: Serves as a new type of gene delivery vector, efficiently transporting gene fragments into nuclei for gene editing and cancer treatment.
- Anti-Aging Research: Directly activates repair mechanisms at the cellular level, potentially reversing aging processes.
Table 1. Comparison of high, medium, low, and ultra-low molecular weight hyaluronic acid: HA with different molecular weights has different water solubility, viscoelasticity, and uses.
Read more: Comparative Analysis of Hyaluronic Acid with Different Molecular Weights
Production Method: Microbial Fermentation
The microbial fermentation method employs microorganisms such as streptococci to produce sodium hyaluronate through fermentation. This process is more eco-friendly and safer than traditional animal tissue extraction, avoiding allergic risks from animal sources. It also allows precise control of molecular weight and purity, meeting diverse industry needs.
Read more: How is Hyaluronic Acid Powder Made
Derivatives of Hyaluronic Acid
To expand the applications of sodium hyaluronate, scientists have developed various derivatives through chemical modifications. For example, cross-linked hyaluronic acid is a derivative where molecular chains are connected with cross-linking agents to form a more stable 3D network structure.
These modifications significantly enhance its resistance to degradation while maintaining elasticity and water retention. Cross-linked hyaluronic acid is primarily used in long-lasting cosmetic fillers for wrinkle removal and shaping. It is also used in joint cavity injections to increase lubrication and alleviate pain.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a pioneer in the development of hyaluronic acid. Products include food-grade, medical-grade, cosmetic-grade, injectable-grade hyaluronic acid, and hyaluronic acid derivatives (Sodium Acetylated Hyaluronate and Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid Gel). We can also provide customers with customized molecular-weight sodium hyaluronate powder. For more information or specific applications, please visit our homepage.