The post Medical-Grade Hyaluronic Acid: From Ophthalmic to Multidisciplinary Therapeutic Agent appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>In general, HA is categorized into different grades based on the application. Besides the usual cosmetic grade, medical-grade, food-grade, and injectable-grade HA also have extensive market applications. We have already touched on the variations between these types of hyaluronic acid. If you’re curious, click on the following link to learn more: Medical Grade vs. Cosmetic Grade Hyaluronic Acid: What Are the Differences.
HA was first discovered to be added to medicine over 70 years ago. It has continued to be a constantly increasing part of life sciences and medicine through continued research.
Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid Was First Used in Ophthalmology
Hyaluronic acid is a multi-purpose matrix that occurs widely in the human body. It possesses a good lubricant and biocompatibility. Medically, it is referred to as sodium hyaluronate and is utilized in various ophthalmic surgeries, such as intraocular lens implantation, corneal transplantation, and glaucoma surgery.
Actually, the therapeutic application of HA dates back 70 years. HA was first successfully used in eye surgeries in the 1950s and remains a common practice to this day. Two decades later, HA’s moisturizing property was beautifully utilized by veterinarians when they filled horse joints with HA to improve mobility. Since then, HA has steadily expanded its role in medicine.
Read more: From Surgery to Daily Care: The Versatile Role of Sodium Hyaluronate in Eye Health
The Diverse Benefits of Medical-Grade Hyaluronic Acid
Presently, with more and more research, applications of HA in medicine are growing day by day. Besides its traditional use in ophthalmology, HA has become a major treatment modality for orthopedic conditions. In osteoarthritis and frozen shoulder, joint lubrication is greatly improved by HA injections, and cartilage is protected.
Moreover, HA use now includes gynecology, tendon fixation, and abdominal surgery, wherein it is utilized as a postoperative device. Its bioadhesive nature allows it to form a protective coating over wounds, both as a lubricant and as a mechanical coating to give the optimal environment for healing.[i] Lastly, HA supplementation is now a standard therapy for cystitis and urinary tract infection, significantly alleviating signs and symptoms with its mucosal protective effect.
HA is also pushing vaccine technology forward. By some chemical manipulations, HA holds pioneering promise as an adjuvant. When mixed with antigens, it enhances antigen-presenting efficacy, induces targeted migration to lymph nodes, and prevents inflammation at the injection site[ii]—offering new conceptual paradigms for vaccine design.
The Role of Hyaluronic Acid Depends on Its Molecular Weight
Low-molecular-weight HA (LMW-HA) can penetrate tissues better, possesses fine bioactivity, and is, therefore, good for anti-inflammatory and tissue repair. Medium-molecular-weight HA (MMW-HA) offers a balance between lubrication and structure. High-molecular-weight HA (HMW-HA) excels in viscoelasticity and water retentive properties. Each of the molecular weight forms has something special to offer—no one “best” one, merely the best for a given purpose. Each has a specific molecular weight range suited to a specific medical application and functional requirement.
The next table provides a working comparison of HA’s properties demanded and molecular weight associated for various medical applications:
| Application | Key Performance Requirements | Recommended MW | Mechanism of Action |
| Ophthalmic Surgery | – High viscoelasticity
– Pseudoplasticity – Biocompatibility |
High (1,000–3,000 kDa) | – Maintains anterior chamber space
– Protects corneal endothelial cells – Facilitates surgical instrument maneuverability |
| Joint Injection | – Moderate viscoelasticity
– Long-lasting lubrication – Anti-inflammatory effects |
Medium (500–1,500 kDa) | – Reduces joint friction
– Inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β) – Stimulates endogenous HA synthesis |
| Wound Healing | – Tissue permeability
– Cell-activating capacity – Angiogenic promotion |
Low (<50 kDa) | – Activates CD44/TLR4 receptors to promote repair
– Accelerates fibroblast migration – Modulates macrophage polarization |
| Vaccine Adjuvant | – Immune cell targeting
– Enhanced antigen presentation – Low inflammatory response |
Low (10–200 kDa) | – Promotes dendritic cell uptake
– Enhances lymph node targeting – Activates immune response via TLR4 |
| Anti-Adhesion Barrier | – Mechanical separation
– Controlled degradation – Tissue compatibility |
Medium-High (1,000–2,000 kDa) | – Physically isolates wound surfaces
– Degrades slowly (4–6 weeks) – Reduces fibrin deposition |
This structured comparison serves as a reference for clinical decision-making or product development, emphasizing that optimal HA selection depends on specific medical requirements.
[i] Belluco C, Meggiolaro F, Pressato D, Pavesio A, Bigon E, Donà M, Forlin M, Nitti D, Lise M. Prevention of postsurgical adhesions with an autocrosslinked hyaluronan derivative gel. J Surg Res. 2001 Oct;100(2):217-21. doi: 10.1006/jsre.2001.6248. PMID: 11592796.
[ii] Jiang D, Liang J, Noble PW. Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases. Physiol Rev. 2011 Jan;91(1):221-64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00052.2009. PMID: 21248167; PMCID: PMC3051404.
The post Medical-Grade Hyaluronic Acid: From Ophthalmic to Multidisciplinary Therapeutic Agent appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Why Hyaluronic Acid is an Ideal Material for Wound Healing appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>What is Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (Hyaluron, HA) is a naturally occurring polysaccharide molecule found in humans and other organisms. It is widely distributed in the human body, primarily present in the skin, joint fluid, eyes, and connective tissues.
HA Structure
The basic structure of hyaluronic acid consists of two types of sugar molecules arranged alternately:
- D-Glucuronic Acid (GlcA)
- N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (GlcNAc)
These two monosaccharides are alternately connected with β-1,3 and β-1,4 glycosidic linkages to disaccharide repeating units. This specific linkage allows HA to possess a linear, unbranched conformation, which avoids branching and complex three-dimensional arrangements, ensuring its high water capacity and fluidity. The carboxyl and hydroxyl groups provide opportunities for HA chemical modification. Hence, it can be synthesized into various hydrogels, fillers, and biomedical materials for various applications.
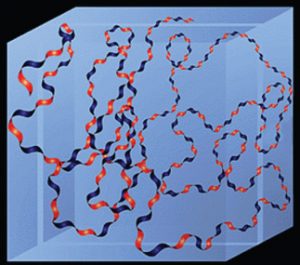
Fig 1. Hyaluronan hydrophilic properties[1]
HA Physiological Functions
As mentioned earlier, hyaluronic acid exists in tissues such as the skin, joints, and eyes in the human body, where it performs important functions:
- Skin: Protects the moisture and elasticity of the skin, softens wrinkles, and delays aging.
- Joints: Lubricates joints, reduces friction, and alleviates arthritis symptoms.
- Eyes: Aids in maintaining the shape and lubrication of the eyeball.
Besides this, hyaluronic acid also serves an important physiological function of wound healing.
Why Hyaluronic Acid Can Heal Wounds
Hyaluronic acid is naturally present in the human body. Endogenous HA and exogenous HA are chemically extremely close. Therefore, the application of hyaluronic acid products in wound healing reduces immune system recognition and rejection reactions. Furthermore, HA is a biodegradable compound, which is degraded by hyaluronidases over time, preventing the accumulation and potential toxicity of the compound in the body. In general, hyaluronic acid is safe, non-toxic, and bio-metabolizable, providing the foundation for it to act as a material in wound healing.
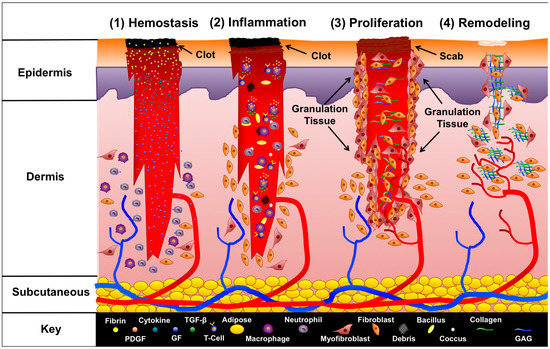
Of course, biocompatibility is just a foundation; the important thing is that hyaluronic acid plays in a number of different functions during the wound healing process through various mechanisms.
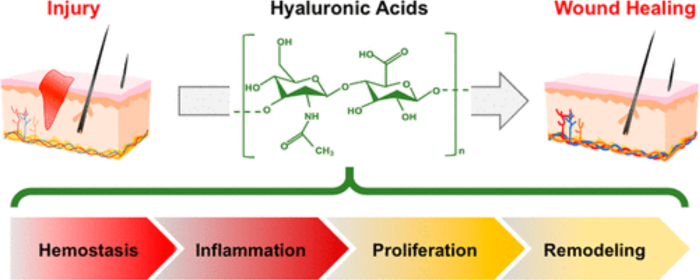
Fig 2. Wound healing process[2]
1. Hemostasis
Hemostasis is the first step in wound healing. The mechanism of hemostasis is to stop bleeding by platelet aggregation and blood clotting, sealing the wound from infection. HA can bind to CD44 receptors on the platelet surface, promoting platelet activation and aggregation, and blood clot formation. In addition, HA’s high molecular weight and viscoelasticity allow it to form a viscous physical barrier on the wound surface, restricting blood loss.
2. Inflammatory Phase
During this phase, inflammatory mediators are released so that leukocytes and other immune cells can migrate into the wound site. They suppress infection, debride the wound, and create good conditions for tissue repair and regeneration. During this phase, the primary role of HA is to induce the migration and proliferation of inflammatory cells. While this increases the inflammatory response, exogenous HA also has anti-inflammatory activity. Some studies show that exogenous HA has been found to reduce the infiltration of inflammatory cells and decrease the inflammatory response. In conclusion, HA guarantees the wound healing is enhanced by the optimal amount of inflammation.
3. Proliferation Phase
The proliferation phase is the critical phase of healing wounds, including angiogenesis, epithelial cell migration and proliferation, and repair of extracellular matrix. During this phase, HA plays a range of roles:
- Promotes Cell Migration and Development: HA triggers fibroblast and epithelial cell proliferation, enabling the wound to close rapidly.
- Promotes Angiogenesis: HA stimulates the growth of new blood vessels to supply new tissue with oxygen and nutrients.
- Enables Extracellular Matrix Development: HA stimulates the production of collagen, reconstitutes tissue structure, and enhances wound strength.
- Retains the Wound Moist: HA keeps the wound in a moist state to enable cell functioning and infection prevention, thereby accelerating healing.
4. Remodeling Phase
The remodeling stage is the final phase of the healing process. In this stage, HA takes part in control of reorganization of collagen to make tissue tougher and elastic as well as preclude scar formation. The previously mentioned anti-inflammatory properties of HA continue to play a role in this phase. It can reduce local inflammation in the wound, promoting the recovery of healthy tissue. Moreover, HA can also promote the synthesis of elastin. With the support of elastin, the healed skin experiences less tightness, restoring its original elasticity and flexibility.
What are the Hyaluronic Acid-Based Dressings
Given the powerful healing property of hyaluronic acid, how can researchers disregard it? Its most common applications are HA-based dressings.
Hyaluronic acid dressings are medical wound-covering agents composed of sodium hyaluronate (sodium salt of HA) that provide an extremely conducive microenvironment for wound repair. They can also be blended with other substances, such as antimicrobial silver ions, collagen, chitosan, etc. Depending on the applications, they exist in various forms.
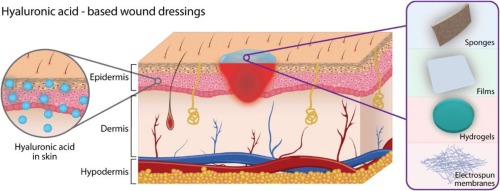
Fig 3. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Dressings[3]
1. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Dressings
Hyaluronic acid hydrogels are the most advanced and versatile type of HA dressings. They are formed through physical or chemical crosslinking, yielding a three-dimensional network hydrophilic gel. They provide a stable moist environment, allowing cell migration and growth. Stable hyaluronic acid hydrogels, for example, can be formed by carbodiimide hydrochloride and adipic dihydrazide crosslinking.
* Suitable for chronic ulcers and burns.
2. Hyaluronic Acid Sponge Dressings
These are highly porous, absorbent dressings. Like a sponge, they are able to suck out excess exudate and prevent maceration. They provide physical support as well, which prevents overgrowth of granulation tissue. They are some of them are mixed with chitosan to enhance antibacterial activity.
* Suitable for highly exudative wounds and postoperative bleeding wounds.
3. Hyaluronic Acid Film Dressings
The most significant benefit of film dressings is their thinness and breathability. With a thickness as low as 0.01~0.1mm, they provide excellent breathability. They are also convenient to apply, sticking to the wound surface without needing secondary fixation.
* Suitable for minimally invasive facial surgeries.
4. Hyaluronic Acid Sprays
These are dressing items that trap sodium hyaluronate in liquid form in pressurized cans or pump bottles, which are applied directly to the skin or wound surface as a spray. Their key features include ease of use, immediate moisturization, and rapid film formation. Medical sprays can also be employed to deliver antibiotics or cytokines for selective drug delivery.
* Suitable for large-area burns and oral/nasal mucosal ulcers.
Other than these traditional dressings, with technology increasing, the market also launched 3D-printed custom dressings. These use a bio-ink composed of HA and fibroblasts to print active dressings with precise matching of the wound contour. They can replicate complicated wounds in a very accurate manner, for instance, nasal defects repair.
Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) offers high-quality hyaluronic acid (HA) powder raw materials suitable for the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and research industries. Their HA powder is characterized by high purity, excellent solubility, and a variety of molecular weight options, ensuring outstanding performance across different applications. Whether you need it for moisturizing formulations, injectable fillers, eye drops, or medical dressings, SCC can meet your requirements. For more product information, contact professionals through the Get A Quote.
[1] Frenkel JS. The role of hyaluronan in wound healing. Int Wound J. 2014 Apr;11(2):159-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.01057.x. Epub 2012 Aug 14. PMID: 22891615; PMCID: PMC7950635.
[2] Polizzi, A.; Leanza, Y.; Belmonte, A.; Grippaudo, C.; Leonardi, R.; Isola, G. Impact of Hyaluronic Acid and Other Re-Epithelializing Agents in Periodontal Regeneration: A Molecular Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212347
[3] Mariana F.P. Graça, Sónia P. Miguel, Cátia S.D. Cabral, Ilídio J. Correia, Hyaluronic acid—Based wound dressings: A review, Carbohydrate Polymers, Volume 241, 2020, 116364, ISSN 0144-8617, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116364.
The post Why Hyaluronic Acid is an Ideal Material for Wound Healing appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post The Comprehensive Guide to Hyaluronic Acid appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>I. Hyaluronic Acid for Eyes
1. What are the benefits of hyaluronic acid for the eyes?
Hyaluronic acid is a water-retaining and lubricating substance. It retains moisture in the eyes and lubricates ocular tissues. It also enhances and repairs corneal damage, which brings great relief to symptoms of dryness, irritation, and eye fatigue.
Clinical trials have shown that sodium hyaluronate eye drops (sodium salt of HA) significantly improve discomfort in dry eye patients and promote the healing process of micro damage on the corneal surface.
Reference: From Surgery to Daily Care: The Versatile Role of Sodium Hyaluronate in Eye Health
2. What are applications of hyaluronic acid in eye care?
In ophthalmology, HA is primarily used in two areas: daily eye care and ophthalmic surgical assistance. For daily care, it serves as a key ingredient in artificial tears. In eye surgeries, it acts as a viscoelastic agent to protect intraocular tissues. For specific case studies, please refer to our related articles.
References:
- Hyaluronic Acid: The Ultimate Moisturizer for Dry Eyes
- Sodium Hyaluronate Used in Anterior Segment Eye Surgery
3. Which is better for the eyes: hyaluronic acid or ectoine?
Both HA and ectoine are excellent eye care ingredients, but they work differently. Hyaluronic acid primarily functions through physical water retention, while ectoine is more effective in protecting cells from environmental stress. The choice depends on specific eye conditions. For a detailed comparison, please refer to our dedicated article.
Reference: Sodium Hyaluronate vs. Ectoine: Which Is Better for Skin and Eyes?
Product Recommendations
Stanford Chem Company (SCC) provides pure medical-grade HA powder specifically developed for ophthalmic applications.
| Product Code | Molecular Weight (Da) | Intrinsic Viscosity (m³/kg) |
| HA-EM2.0-SC | 800K–1,300K | 1.44–2.12 |
| HA-EM2.4-SC | 1,300K–1,800K | 2.12–2.72 |
| HA-EM3.0-SC | 1,800K–2,500K | 2.72–3.53 |
| HA-EMC-SC | Customized | Customized |
II. Hyaluronic Acid for Skin

1. How strong is hyaluronic acid’s hydrating ability?
Hyaluronic acid is known as the “natural moisturizing factor” due to its exceptional water-binding capacity. Scientific data shows that 1 gram of HA can hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, making it an essential hydrating ingredient in skincare.
2. What are the benefits of hyaluronic acid for skin?
Beyond its superior moisturizing effects, HA also promotes skin barrier repair and improves elasticity. Recent studies suggest it may delay skin aging by regulating specific signaling pathways, opening new possibilities for anti-aging product development.
Reference: What Does Sodium Hyaluronate Do for the Skin?
3. Is a lower molecular weight always better?
There is a common misconception that the lower the molecular weight, the better and that molecules over 500 Da are too large to penetrate the skin. However, different molecular weights offer different benefits, and larger molecules can still permeate through advanced formulation techniques. A 2024 study found that high-molecular-weight HA penetrates the skin effectively, providing anti-inflammatory, reparative, and antioxidant effects.[1]
Therefore, molecular weight selection should be informed by science. The ideal product should comprise a mixture of HA with various molecular weights.
4. Hyaluronic acid vs. collagen: Which one should you choose?
These two ingredients work differently—HA primarily hydrates, while collagen provides structural support. The best approach is to use them together for synergistic effects, as detailed in our research article.
Reference: Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen: The Perfect Combination for Healthy Skin
5. Hyaluronic acid, retinol, and vitamin C: Which is best for skincare?
Each of these active ingredients excels in different areas: HA for hydration, retinol for wrinkle reduction, and vitamin C for antioxidant protection. The choice depends on skin needs and tolerance, and sometimes combining them yields better results. Our comparative study provides detailed usage recommendations.
Reference: Hyaluronic Acid vs. Retinol vs. Vitamin C: Which Is Best for Skincare?
6. Can hyaluronic acid cause acne?
Pure HA itself does not cause acne, as it is non-comedogenic. However, some HA products may contain other additives that could trigger breakouts. Always check the full ingredient list, especially if you have oily or acne-prone skin.
Reference: Can Hyaluronic Acid Cause Acne?
Product Recommendations
Our cosmetic-grade sodium hyaluronate powder features high purity with minimal impurities. Compared to other market products, it contains higher glucuronic acid content and lower levels of protein, heavy metals, and nucleic acids.
| Product Code | Molecular Weight (Da) | Classification |
| HAC-Micro-SC | <5K | Ultra-Low Molecular Weight |
| HAC-Oligo-SC | 5K–10K | Low Molecular Weight |
| HAC-N-SC | 200K–600K | Standard |
| HAC-L-SC | 100K–1,000K (800K) | Broad Range |
| HAC-M-SC | 800K–1,600K | Medium Molecular Weight |
| HAC-H-SC | >1,800K | High Molecular Weight |
| HAC-C-SC | Customized | Custom Molecular Weight |
III. Hyaluronic Acid for Joints
1. Why is hyaluronic acid able to relieve arthritis?
Hyaluronic acid is a major component of synovial fluid, producing lubrication and cushioning in joints. In patients with arthritis, the concentration and molecular weight of HA in joint fluid are reduced. Exogenous sodium hyaluronate supplementation can improve joint function and relieve pain symptoms.
2. Hyaluronic acid or chondroitin sulfate: Which is better for joints?
Both supporters ensure joint health but differently. HA primarily facilitates joint lubrication, while chondroitin sulfate is all about cartilage protection. They are usually prescribed clinically together for general joint support.
Reference: Hyaluronic Acid vs. Glucosamine vs. Chondroitin: Which Is Best for Joints?
3. Does oral hyaluronic acid alleviate joint pain?
The oral bioavailability of HA has been a subject of research emphasis. The clinical evidence available presently suggests that certain molecular-weight oral HA is incompletely absorbed but demonstrates improvement of joint symptoms, though its effects are typically more delayed compared to injections.
4. What are the side effects of hyaluronic acid joint injections?
Intra-articular HA injection is also safe. Injection-site pain or inflammation is a common mild reaction occasionally seen in a few patients. Severe side effects are exceedingly rare.
Product Recommendations
Our injection-grade HA is mainly used for intra-articular and intraocular injections. It also serves in orthopedic surgery, human/animal (e.g., horses, dogs) joint dysfunction treatment, post-surgical adhesion prevention, and drug delivery.
| Product Code | Molecular Weight (Da) | Intrinsic Viscosity (m³/kg) |
| HA-EP1.8-SC | 800K–1,300K | 1.44–2.12 |
| HA-EP2.4-SC | 1,300K–1,800K | 2.12–2.72 |
| HA-EP3.0-SC | 1,800K–2,500K | 2.72–3.53 |
| HA-EPC-SC | Customized | Customized |
IV. Hyaluronic Acid for Scalp

1. Is hyaluronic acid good for hair?
Yes. HA preserves scalp moisture and enhances hair luster. It really makes a big difference for hydrating hair, particularly dry or damaged hair.
2. Can normal hyaluronic acid be applied to the scalp?
Skincare-grade HA can be applied to the scalp, but concentration and formulation are important. For best outcomes, use hair-care products formulated specifically considering scalp physiology.
3. Is hyaluronic acid in shampoos safe?
HA shampoos are safe. Keep in mind that other shampoo ingredients can have an impact on HA stability. Always test the whole formula for compatibility.
Conclusion
We hope this guide helps you understand and use hyaluronic acid products more effectively. For professional inquiries, please contact us: Get A Quote.
[1] Hui Xing, Xiangjun Pan, Yihan Hu, High molecular weight hyaluronic acid-liposome delivery system for efficient transdermal treatment of acute and chronic skin photodamage, Acta Biomaterialia, Volume 182, 2024, Pages 171-187, ISSN 1742-7061, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2024.05.026.
The post The Comprehensive Guide to Hyaluronic Acid appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Guides to Hyaluronic Acid Injections appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>1. Why Choose Hyaluronic Acid for Injections?
Hyaluronic acid is favored for injections because of its exceptional biocompatibility and lubricating properties. As a naturally occurring polysaccharide in the human body, HA is widely distributed in the skin, joints, and connective tissues, providing superior hydration and lubrication.
In cosmetics, HA is used to:
✓ Fill facial wrinkles
✓ Enhance facial volume
✓ Improve skin elasticity by replenishing moisture for a youthful, smooth appearance
In joint treatments, HA:
✓ Increases synovial fluid viscosity
✓ Improves joint lubrication and shock absorption
✓ Alleviates arthritis symptoms
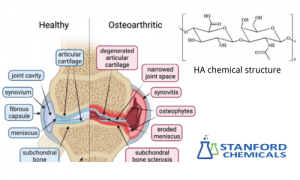
Thanks to its high safety profile and low risk of immune reactions, HA is a top choice for injectable treatments.
2. Which Body Parts Can Receive Hyaluronic Acid Injections?
HA injections are versatile, targeting multiple areas with distinct purposes and effects.
The table below summarizes the main applications of sodium hyaluronate in different areas of the body:
| Injection Site | Primary Use | Expected Outcome |
| Face | Wrinkle filling, contour lifting, lip augmentation | Improved skin elasticity, enhanced facial aesthetics |
| Hands | Volume restoration | Youthful, fuller-looking hands |
| Neck | Skin tightening, fine line reduction | Smoother necklines, reduced wrinkles |
| Joints | Pain relief, improved mobility | Better joint function, reduced discomfort |
3. What Is the Difference between Cosmetic Injections and Joint Injections?
Although both cosmetic injections and joint injections use hyaluronic acid as the primary material, there are significant differences in the types of hyaluronic acid used and injection techniques due to their different purposes and treatment goals.
Cosmetic injections are primarily aimed at improving appearance, such as reducing wrinkles, enhancing facial contours, and increasing lip volume. Common injection sites include the face, hands, lips, and neck – areas that require aesthetic enhancement. To achieve durable yet natural-looking results, cosmetic injections typically utilize high molecular weight (>1000kDa) cross-linked hyaluronic acid, which offers superior filling capacity and longer-lasting effects. However, the formulation must be carefully customized according to the treatment area (for example, lower cross-linking for lip injections) and individual tissue characteristics. Furthermore, cosmetic injections demand highly precise technique from practitioners to ensure natural-looking results while avoiding asymmetry or nodule formation.

In contrast, joint injections primarily focus on relieving pain and improving joint function by enhancing synovial fluid lubrication. The molecular weight selection depends on the arthritis stage. Low molecular weight HA provides rapid anti-inflammatory effects in early stages, while moderate-to-high molecular weight or cross-linked HA is preferred for advanced cases to optimize lubrication and shock absorption. Joint injections require even greater technical precision, as practitioners must accurately deliver HA into the joint space with exact depth and positioning to achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes.
4. How Does the Purity of Hyaluronic Acid Affect Injection Results?
The purity of hyaluronic acid directly affects the safety and efficacy of the injection. High-purity hyaluronic acid contains fewer impurities and potential allergens, which not only reduces the risk of allergic reactions and adverse effects but also ensures its longevity and biocompatibility within the body.
5. How Does the Molecular Weight of Sodium Hyaluronate Affect Injection Results?
The molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate determines its physical properties and therapeutic effects within the body.
| Parameter | High Molecular Weight (>1000kDa) | Low Molecular Weight (<100kDa) |
| Core Advantage | Structural support/Deformation resistance | Rapid penetration/Biological activity |
| Rheological Properties | High G’ modulus (Elasticity) | High fluidity |
| Optimal Application | Nasal base/jawline shaping | Epidermal hydration/Dermal regeneration treatments |
| Duration | 12-24 months (requires cross-linking) | 1-3 months (non-cross-linked) |
| Risk Warning | Overfilling leading to a “mask-like” appearance | High swelling risk (high water absorption) |
How to choose?
High molecular weight hyaluronic acid (when combined with cross-linking) is indeed more suitable for deep-layer filling, but its core advantage lies in mechanical support rather than mere water absorption capability. Low molecular weight HA excels in permeability and biological activity but requires attention to its potential inflammatory risks. Clinical selection should comprehensively consider molecular weight, degree of cross-linking, and injection depth, rather than relying on a single parameter.
6. How Does the Solubility of Hyaluronic Acid Affect Injection Results
Choosing the appropriate solubility of hyaluronic acid is crucial for achieving the desired injection outcomes. Highly soluble hyaluronic acid is more suitable for areas requiring fine, natural effects, while low solubility products should be used with caution, typically in conjunction with professional injection techniques to avoid adverse reactions. The injection effects of different solubility HA are as follows:
Highly Soluble Hyaluronic Acid:
- Uniform Distribution: Can spread more evenly in the injection area, reducing the risk of local lump formation.
- Natural Filling Effect: Ensures a smooth skin surface post-injection, making it difficult to detect granularity or irregular lumps.
- Balanced Absorption: Aids in the uniform absorption of hyaluronic acid within the body, prolonging maintenance time.
Low Solubility Hyaluronic Acid:
- Easily Forms Granules: May result in noticeable granules or nodules during the injection process, affecting aesthetics.
- Uneven Filling: Can cause localized bulges or depressions, impacting the overall effect.
- Increased Irritation: Local accumulation might trigger inflammation or discomfort.
7. What Are the Advantages of Cross-Linked HA Gels?
Cross-linked HA gel are the preferred material in cosmetic injections because they can provide patients with more lasting and natural aesthetic results. Cross-linked hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels form a stable cross-linked structure between HA molecules through chemical or physical methods. This cross-linked structure enhances the mechanical strength and durability of the HA hydrogel, slowing its degradation rate within the body and extending the longevity of the injection effects. Moreover, cross-linked HA hydrogels can better maintain their shape after injection, reducing diffusion and migration. What’s more, the cross-linking process can further purify HA, removing impurities and lowering the risks of immune reactions and allergic responses.
8. How Long Do Hyaluronic Acid Injections Last for the Knee and Face?
The duration of HA injections depends on the treatment area and individual factors such as metabolism, activity level, and the specific HA product used. Generally, the duration is as follows:
| Injection Site | Purpose | Duration | Influencing Factors |
| Knee Joint | Alleviate joint pain, improve joint function | 6 months to 1 year | Degree of joint degeneration, activity level, overall joint health |
| Face | Fill wrinkles, enhance facial contours, increase lip volume | 6 months to 2 years | Injection area, skin quality and age, lifestyle factors (e.g., sun exposure, smoking) |
9. What Are the Side Effects of Hyaluronic Acid Injections?
Due to the biocompatibility of hyaluronic acid (HA), injections of HA are generally considered safe. However, like any medical procedure, they may produce potential side effects. Common side effects include:
Local Reactions:
- Redness and Swelling: Temporary inflammation at the injection site.
- Pain and Tenderness: Mild discomfort during and after the injection.
- Bruising: Minor bruising may occur at the injection site.
Rare Side Effects:
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions, including itching, rash, or hives.
- Lumps and Bumps: Small lumps or nodules may form subcutaneously, which might require massaging and, in extremely rare cases, medical intervention.
- Infection: As with any injection, there is a slight risk of infection at the injection site.
- Vascular Occlusion: A very rare but severe complication where HA is inadvertently injected into a blood vessel, potentially causing tissue necrosis or vision problems if it occurs near the eyes.
Mitigation Measures:
- Experienced Practitioners: Ensure that injections are performed by qualified and experienced medical professionals to minimize risks.
- Proper Disinfection: Maintain a sterile environment to reduce the risk of infection.
- Patch Testing: Conduct skin tests on individuals known to be allergic to HA or related substances.
Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) is a professional supplier of hyaluronic acid. SCC offers high-purity, high-quality, and safe sodium hyaluronate powder (including food-grade, cosmetic-grade, medical-grade, and injectable-grade). All of SCC’s hyaluronic acid products are made using the bacterial fermentation method, ensuring safety and reliability.
The post Guides to Hyaluronic Acid Injections appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post The Application of Chondroitin Sulfate in Eye Care appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>Why Chondroitin Sulfate Works for Eye Care
Chondroitin sulfate is suitable for eye care due to its unique biochemical properties and multiple benefits for eye tissues. It has excellent moisturizing abilities, effectively keeping the eye’s mucous membranes hydrated and reducing dryness and discomfort. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties help soothe eye inflammation and protect eye tissues from free radical damage. These qualities make chondroitin sulfate an ideal active ingredient in eye drops, especially for managing conditions like dry eye syndrome.
Benefits of Chondroitin Sulfate for the Eyes
- Promotes Cell Repair: It aids in the regeneration and repair of eye cells, boosting the tissue’s self-healing ability.
- Antioxidant Protection: By neutralizing free radicals, it protects eye cells from oxidative stress and delays eye aging.
- Strengthens the Eye Barrier: It enhances the mucous membrane’s barrier function, preventing harmful substances from entering and reducing infection risks.
- Moisturizing and Lubricating: It locks in moisture, keeping the eye’s mucous membranes hydrated.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Its anti-inflammatory properties help reduce redness, swelling, and irritation.
Chondroitin Sulfate vs. Sodium Hyaluronate
Both sodium hyaluronate and chondroitin sulfate are common ingredients in eye drops, excelling in moisturizing and lubrication. However, they differ in specific functions and applications.
Sodium hyaluronate can absorb large amounts of water, providing long-lasting lubrication and high viscoelasticity. It forms a stable protective layer on the eye, reducing discomfort caused by friction. This makes it ideal for dry eye patients needing intense hydration. In contrast, while chondroitin sulfate also offers excellent moisturizing, it focuses more on maintaining the natural hydration of the eye’s mucous membranes. Its moderate viscoelasticity provides a more comfortable lubrication experience.
Additionally, chondroitin sulfate has stronger anti-inflammatory and cell repair benefits, making it stand out. Beyond hydration, it helps reduce inflammation and enhances tissue repair, making it suitable for users who need both hydration and anti-inflammatory support.
Chondroitin Sulfate vs. Ectoine
Ectoine is a natural compatible solute known for its exceptional moisturizing and cell-protecting abilities, widely used in eye drops. Compared to chondroitin sulfate, Ectoine excels in hydration, quickly relieving dryness and maintaining cellular water balance. It protects cells by stabilizing their structure and defending against environmental stressors like dryness and pollution.
However, chondroitin sulfate offers superior repair capabilities. It not only protects cells but also promotes their regeneration and repair. Its anti-inflammatory properties are also more pronounced, effectively reducing eye inflammation. In contrast, Ectoine focuses more on cell protection and stability, with only mild anti-inflammatory effects.
In short, Ectoine provides lightweight hydration, ideal for quick relief from dryness, while chondroitin sulfate offers comprehensive eye care, better suited for long-term use and multi-faceted needs.
Read more: Sodium Hyaluronate vs Ectoine: Which is Better for Skin and Eyes
Other Applications of Chondroitin Sulfate
Beyond eye care, chondroitin sulfate has unique value in several fields:
- Joint Health: As a dietary supplement, it’s widely used to ease joint pain and improve joint function, often combined with glucosamine.
- Skincare: In skincare products, it boosts hydration, promotes skin cell regeneration, and reduces fine lines and wrinkles.
- Cardiovascular Health: Studies show it helps lower blood lipids, improve vascular elasticity, and prevent atherosclerosis.
- Digestive Health: As a dietary fiber, it supports gut health and aids digestion and absorption.
- Oral Care: In oral care products, it improves saliva quality, preventing dry mouth and cavities.
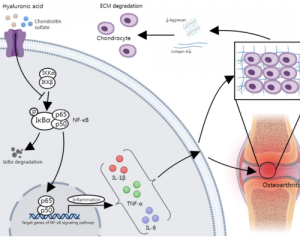
Fig 2. Combined use of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate for osteoarthritis relief[1]
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is an excellent supplier of sodium hyaluronate powder and chondroitin sulfate. In addition, we also provide ectoine powder for cataract surgery eye drops and joints. For more information on these materials, please Get A Quote.
FAQs About Chondroitin
- Is Chondroitin Sulfate Eye Drops Suitable for Everyone?
Chondroitin sulfate-based eye drops are suitable for most dry eye patients, especially those with dryness caused by prolonged screen use, contact lenses, or dry environments. However, pregnant or breastfeeding women, or those with specific eye conditions, should consult a doctor before use.
- Are There Side Effects of Using Chondroitin Sulfate Eye Drops?
It’s generally considered safe, with minimal side effects. A few users may experience temporary irritation or mild discomfort, such as a burning sensation or blurred vision, which usually subsides within minutes. If severe discomfort occurs, discontinue use and seek medical attention.
- How Compatible Is Chondroitin Sulfate with Other Ingredients?
Chondroitin sulfate works well with various moisturizers and anti-inflammatory agents, such as sodium hyaluronate and Ectoine. The synergy between these ingredients provides more comprehensive eye care. Choosing a product with a tailored combination of ingredients can enhance the overall experience.
- What is chondroitin sulfate in ophthalmology?
Chondroitin sulfate is used in ophthalmology as a moisturizing and anti-inflammatory agent in eye drops, particularly for treating dry eye syndrome and protecting eye tissues.
- Does chondroitin raise eye pressure?
No, chondroitin sulfate does not raise eye pressure. It is generally safe and used to support eye health.
- Is chondroitin sulfate an anti-inflammatory?
Yes, chondroitin sulfate has anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation in tissues, including the eyes.
- Does glucosamine chondroitin affect sleep?
There is no strong evidence that glucosamine chondroitin directly affects sleep. However, individual reactions may vary.
[1] Ma, Y., Yang, X., Jiang, M. et al. Alone or in combination, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate alleviate ECM degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. J Orthop Surg Res 20, 11 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-024-05411-6
The post The Application of Chondroitin Sulfate in Eye Care appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Top 7 Powerful Benefits of Fisetin appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>Fisetin (C₁₅H₁₀O₆) is a natural flavonoid compound. It can be extracted from the lacquer tree and is widely found in vegetables and fruits such as strawberries, apples, onions, and cucumbers. Fisetin is a yellow crystalline powder that is nearly insoluble in water but easily soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, acetone, and acetic acid.
It is also a high-molecular pharmaceutical raw material with diverse uses. It can be utilized in the development of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer drugs, as well as serving as an antioxidant and immune booster. What’s more, it is used in cosmetics for its anti-aging properties.
Table 1. Physicochemical Properties of Fisetin
| Property | Value |
| Molecular Formula | C₁₅H₁₀O₆ |
| Molecular Weight | 286.24 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow crystalline powder |
| Melting Point | Approximately 330°C (decomposition) |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble/insoluble in water; soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone, DMSO |
| Acidity/Alkalinity | Weakly acidic |
| Stability | Sensitive to light and heat |
| Reactivity | Easily chelates with metal ions; exhibits antioxidant activity |
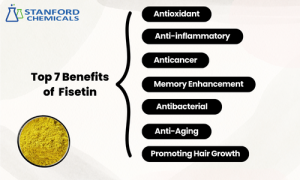
1. Antioxidant: The Mighty Guardian Against Oxidation
It boasts strong antioxidant capabilities, offering numerous benefits.
–Fisetin Benefits in Antioxidant
Fisetin neutralizes free radicals and reduces oxidative stress-induced cellular damage. Studies show it enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the body, lowering oxidative stress levels and protecting cells from oxidative damage.
–Applications Based on Antioxidant Properties:
Fisetin’s potent antioxidant capacity holds vast potential in pharmaceuticals, health supplements, cosmetics, and the food industry.
- Drug Development: Used in the development of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and neuroprotective drugs.
- Dietary Supplements: Acts as an antioxidant and immune booster, enhancing immunity and delaying aging.
- Anti-Aging Products: Incorporated into anti-aging and antioxidant skincare products to protect the skin from free radical damage.
- Natural Antioxidant: Used as a food additive to extend shelf life and maintain freshness.
2. Anti-Inflammatory: Relieving Inflammation Troubles
Fisetin exhibits significant anti-inflammatory effects, making it a potential candidate for novel anti-inflammatory drugs.
–How Fisetin Fights Inflammation
Fisetin primarily modulates multiple inflammation-related signaling pathways and molecules:
- Inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators and reduces the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6).
- Suppresses NF-κB activation, reducing its translocation to the nucleus and lowering the expression of inflammation-related genes.
- Inhibits MAPK signaling pathways (e.g., ERK, JNK, p38 MAPK), reducing the production and release of inflammatory mediators.
- Suppresses the activation of immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils, decreasing their release of inflammatory mediators.
–Applications Based on Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Fisetin shows significant value in treating inflammation-related diseases, managing chronic inflammation, and developing anti-inflammatory products. It alleviates inflammatory responses, reducing pain and discomfort. Currently, it is a common ingredient in anti-inflammatory and pain-relief medications and offers potential for treating arthritis, neuroinflammation, and cardiovascular inflammation.[1]
3. Memory Enhancement: The Brain’s Natural Booster
Research shows that fisetin improves memory and cognitive function in aging animals.

–Why Does Fisetin Enhance Memory
Fisetin offers multifaceted benefits for the brain and memory. Its antioxidant properties protect the brain from oxidative damage. Like other flavonoids, it increases glutathione (GSH) levels in brain cells. Glutathione is a critical antioxidant vital for brain cell function and health, and its levels directly impact antioxidant capacity, inflammation response, detoxification, and overall brain health.
Additionally, fisetin promotes the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a substance that supports neuron survival, growth, and synaptic plasticity. Elevated BDNF levels enhance learning and memory. Fisetin also modulates multiple memory-related signaling pathways, such as regulating NMDA receptor activity to promote synaptic plasticity, thereby improving memory. Furthermore, it enhances mitochondrial energy metabolism, ensuring sufficient energy supply for brain cells and supporting normal brain function.
–Applications for Memory Enhancement:
- Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment: Improves memory and cognition, slowing disease progression in conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Brain Injury Repair: Promotes neural repair and functional recovery post-injury through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Memory-Boosting Supplements: Dietary supplements to enhance memory and focus in the elderly, students, and professionals.
- Functional Foods: Beverages and snacks that help consumers incorporate fisetin into their daily diet for improved memory.
4. Antibacterial: A Natural Antimicrobial Powerhouse
Fisetin effectively inhibits the growth of various bacteria, disrupts bacterial cell structures, and reduces infection risks.
–Fisetin Benefits in Antimicrobial
Fisetin inhibits multiple bacteria and fungi, including E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It also prevents bacterial biofilm formation, reducing bacterial attachment and proliferation, thereby lowering infection risks.
Antimicrobial Mechanisms:
- Disrupts bacterial cell membrane integrity, causing cell content leakage and bacterial death.
- Inhibits key bacterial enzyme activity, interfering with metabolic processes and bacterial growth.
- Disrupts bacterial DNA replication, inhibiting bacterial proliferation.
–Applications Based on Antimicrobial Effects:
Fisetin holds vast potential in natural preservatives and anti-infection products.
- Antimicrobial Drug Development: A candidate molecule for novel antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
- Antimicrobial Skincare: Used in skincare products to prevent and treat skin infections like acne and fungal infections.
- Natural Preservative: Extends the shelf life of food products.
5. Anticancer: Inhibiting Tumor Growth and Spread
Fisetin offers multiple benefits in cancer prevention and treatment.
–Benefits of Fisetin in Anticancer
Fisetin reduces cancer risk by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways, thereby lowering oxidative damage and inflammation. It activates apoptosis pathways, inducing programmed cell death in cancer cells while sparing normal cells. Fisetin also inhibits VEGF and related signaling pathways, reducing tumor angiogenesis and limiting tumor growth and spread. It synergizes with chemotherapy drugs, enhancing anticancer effects and reducing side effects.
–Applications Based on Anticancer Effects
- Adjuvant Cancer Therapy: Used alongside chemotherapy or radiotherapy to reduce tumor recurrence.
- Cancer Prevention: Daily intake through diet or supplements helps lower cancer risk.
6. Anti-Aging: Revitalizing Youthful Skin
Fisetin helps maintain youthful and healthy skin.

–Fisetin Benefits for Skin
Fisetin delays skin aging through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, collagen synthesis promotion, barrier function enhancement, and cellular repair. It neutralizes free radicals, protects skin cells from damage, reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine release, stimulates collagen production, and enhances skin barrier function to reduce moisture loss.
–Applications Based on Anti-Aging Effects:
Fisetin is widely used in anti-aging skincare, repair products, and sunscreens.
- Anti-Aging Skincare: Reduces fine lines and wrinkles, improving skin elasticity.
- Repair Products: Repairs skin damage caused by UV rays and pollution.
- Sunscreen Additive: Enhances UV protection in sunscreens.
7. Promoting Hair Growth
In vitro and animal studies show that fisetin significantly promotes hair follicle cell proliferation and extends the hair growth phase (Anagen).
–Fisetin Benefits for Hair
Fisetin creates a healthy environment for hair growth through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. It promotes hair follicle stem cell proliferation and differentiation, extends the Anagen phase, and accelerates hair growth. Additionally, it improves blood circulation to the scalp, enhancing nutrient supply to hair follicles. Fisetin also inhibits 5-α reductase activity, reducing DHT production and preventing androgenetic alopecia.
–Applications Based on Hair Care Effects
- Topical Products: Added to shampoos, conditioners, scalp serums, and hair masks to promote hair growth.
- Oral Supplements: Improves scalp health and promotes hair growth from within.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a premium supplier of hyaluronic acid and herbal extracts. We offer fisetin and pure hyaluronic acid powder (medical-grade, food-grade, cosmetic-grade, injection-grade, and eye-drop-grade). For more information on these products or specific applications, please contact us and visit our homepage.
[1] Pal HC, Pearlman RL, Afaq F. Fisetin and Its Role in Chronic Diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;928:213-244. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41334-1_10. PMID: 27671819.
The post Top 7 Powerful Benefits of Fisetin appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Solubility, Viscosity, and Stability of Sodium Hyaluronate appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>Solubility of Sodium Hyaluronate
The solubility of sodium hyaluronate is the foundation of its application. Solubility not only affects its dispersibility in different solutions but also directly influences its bioavailability and efficacy. The solubility is influenced by various factors, including solvent type, temperature, pH, and the molecular weight of hyaluronic acid.
–How Long Does It Take for Sodium Hyaluronate to Dissolve
The solubility of sodium hyaluronate varies in different solvents. In water, it can dissolve quickly, forming a transparent and viscous solution. In glycerol, its solubility is moderate, though not as high as in water. This is why glycerol and hyaluronic acid are often found together in cosmetics. In ethanol, the solubility of hyaluronic acid is low, and it usually requires mixing with other solvents. In acetone, sodium hyaluronate is almost insoluble and is generally not used in such solvents.
Table 1. A comparison of the solubility of sodium hyaluronate in different solvents:
| Water | Oil | Organic Solvent | Ethanol | Methanol | Alcohol | Glycerine | |
| Solubility | High solubility | Insoluble | Very low to insoluble | Very low to insoluble | Very low to insoluble | Very low to insoluble | Moderate solubility |
| Optimal Temperature | 20-40°C | / | / | / | / | / | 30-40°C |
| Optimal pH | 5.5-7.5 | / | / | / | / | / | 5.5-7.5 |
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a trusted supplier of sodium hyaluronate powder. We provide customers with high-purity, non-animal-derived, non-GMO hyaluronic acid powder (including food grade, cosmetic grade, injection grade, medical grade, eye drop grade, cross-linked gel). Enjoy bulk purchase discounts and contract pricing.
–How to Dissolve Sodium Hyaluronate Quickly
In addition to solvent type, several factors influence the solubility of sodium hyaluronate. A previous article discussed this topic in detail. If interested, you can click to read: Solubility of Hyaluronic Acid in Different Solvents and Its Influencing Factors
To accelerate dissolution, the following methods are commonly used:
- Stirring: Mechanical stirring can speed up the dispersion and dissolution of HA in water. The stirring speed and duration significantly affect the dissolution efficiency.
- Heating: Moderate heating (usually not exceeding 60°C) can increase the dissolution rate, but care must be taken to avoid degradation caused by high temperatures. Temperature should be controlled, and prolonged high-temperature treatment should be avoided.
- Premixing: Premixing sodium hyaluronate with a small amount of glycerol or ethanol before diluting with water can improve dissolution efficiency. This method is particularly suitable for preparing high-concentration sodium hyaluronate solutions.
Viscosity of Sodium Hyaluronate
Viscosity is one of the important physical properties of sodium hyaluronate, directly affecting its application in cosmetics and medicine.
–How Viscosity Affects the Efficacy of Sodium Hyaluronate
The viscosity of hyaluronic acid is closely related to its molecular weight. High-viscosity hyaluronic acid forms a protective film on the skin surface, effectively locking in moisture, while low-viscosity sodium hyaluronate penetrates deeper into the skin, providing deep hydration. Viscosity also affects the flowability and distribution uniformity of sodium hyaluronate during injection or application.
–What Factors Affect the Viscosity of HA
Molecular weight, concentration, temperature, pH value.
Higher molecular weight results in higher viscosity. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid has longer molecular chains and stronger intermolecular interactions, leading to higher viscosity.
Higher concentration leads to higher viscosity. In high-concentration sodium hyaluronate solutions, molecules are closer together, resulting in stronger interactions and increased viscosity.
Higher temperatures reduce viscosity. Increased molecular motion at high temperatures weakens intermolecular interactions, causing a decrease in viscosity.
Hyaluronic acid exhibits the most stable viscosity within a pH range of 6-8. Under acidic or alkaline conditions, sodium hyaluronate molecules may undergo hydrolysis or cross-linking, leading to changes in viscosity.
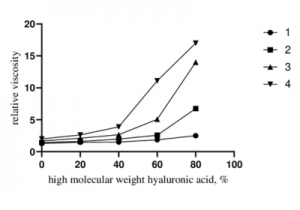
Fig 2. Relationship between the relative viscosity of LMW-HA/HMW-HA aqueous solutions and the HMW-HA content.[1]
Stability of Sodium Hyaluronate
The stability of sodium hyaluronate is another critical factor in its application. Stability not only affects its storage and shelf life but also influences the durability of its efficacy.
The Impact of Temperature on Stability
Hyaluronic acid is prone to degradation at high temperatures, so high-temperature environments should be avoided during storage and use. Typically, sodium hyaluronate is most stable within a temperature range of 4°C to 25°C.
The Impact of pH on Stability
Hyaluronic acid is susceptible to hydrolysis in acidic or alkaline environments, leading to molecular chain breakage. Therefore, maintaining the pH of sodium hyaluronate solutions within the range of 6-8 is crucial for ensuring stability.
The Impact of Light and Oxidation on Stability
Hyaluronic acid is prone to degradation under light and oxidative conditions. Therefore, it should be stored away from light, and antioxidants should be added to extend its stability.
Read more: How to Maintain the Stability of Hyaluronic Acid Products
Table 2 below is a comparison of the stability of HA under different conditions:
| Condition | Stability | Explanation |
| Temperature (4-25°C) | High | Suitable for long-term storage |
| Temperature (>60°C) | Low | Prone to degradation |
| pH 6-8 | High | Suitable for most applications |
| pH <4 or >10 | Low | Prone to hydrolysis |
| Light-protected | High | Prevents degradation |
| Light-exposed | Low | Prone to photodegradation |
| With antioxidants | High | Prevents degradation |
| Without antioxidants | Low | Prone to oxidative degradation |
[1] Saitarly, Svetlana & Pushkarev, Yuriy & Nesterkina, Mariia & Ozturk, Serhat & Salih, Bekir & Kravchenko, Iryna. (2021). Rheological Properties of Hyaluronic Acid Diluted Solutions as Components of Cosmetics. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry. 12. 1907-1915. 10.33263/BRIAC122.19071915.
The post Solubility, Viscosity, and Stability of Sodium Hyaluronate appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Hyaluronic Acid vs. Ceramides: Which Works Better appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>Hyaluronic acid and ceramides are undoubtedly two of the most popular ingredients in the hydration and moisture retention domain. One is a classic ingredient hailed as the “king of hydration,” while the other is a “repair sensation” that has gained popularity in recent years. So, what exactly are the differences between these two ingredients?
Hyaluronic Acid: The “Evergreen Tree” of Hydration
Hyaluronic Acid (HA) is a naturally occurring polysaccharide in the human body, especially abundant in the skin, joints, and eyes. Its most notable feature is its ability to absorb and retain a large amount of moisture, making its moisturizing capacity truly “powerful”—1 gram of hyaluronic acid can absorb up to 1000 grams of water, thus earning the title of “natural moisturizing factor”.
–Mechanism of Action of Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid works by forming a moisturizing film on the surface of skin, helping to lock in moisture. At the same time, it absorbs water from the environment, keeping the skin hydrated. Depending on its molecular weight, it operates at different skin layers:
- High-Molecular-Weight HA: Remains on the skin’s surface, forming a protective barrier to prevent moisture evaporation.
- Low-Molecular-Weight HA: Penetrates deep into the skin, providing internal hydration and increasing the skin’s moisture content.
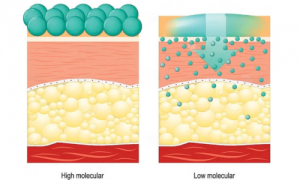
Fig 1. Difference between high and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid
–Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid
HA provides immediate hydration effects. After using products containing hyaluronic acid, the skin instantly feels plump and hydrated, with a significant reduction in dryness. It is suitable for all skin types, whether dry, oily, or combination.
In addition to hydration and moisture retention, HA also has anti-aging benefits. This is because adequate moisture makes the skin appear firmer and can reduce the appearance of fine lines and dry wrinkles.
However, hyaluronic acid also has its limitations. It primarily focuses on hydration and has limited effects on repairing the skin barrier or improving sensitivity issues. If your skin barrier is already damaged, relying solely on hyaluronic acid may not fundamentally resolve the problem.
Ceramides: The “Newcomer Sensation” in Repair
Ceramides are lipids found in the intercellular spaces of the skin’s epidermal cells, constituting approximately 50% of the total intercellular lipids[i]. They are a crucial component of the skin barrier, acting like “cement” to tightly connect skin cells, preventing moisture loss and the intrusion of external irritants.
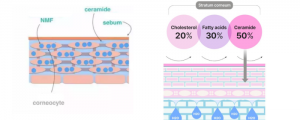
Fig 2. It accounts for about 50%
–Mechanism of Action of Ceramides
Unlike hyaluronic acid, the primary function of ceramides is not hydration but the repair and strengthening of the skin barrier. When the skin barrier is compromised, moisture loss accelerates, and the skin becomes dry, sensitive, and may even develop inflammation. Ceramides replenish the lost lipids in the skin, repair barrier function, thereby locking in moisture and improving the overall health.
–Advantages of Ceramides
For barrier damage caused by excessive cleansing, environmental stressors, or improper skincare, ceramides can effectively repair and restore the skin’s healthy state. Although ceramides do not directly hydrate, they provide moisture retention. By repairing the barrier, ceramides fundamentally reduce moisture loss, offering long-lasting hydration effects.
While ceramides excel in repair and moisture retention, their hydration effects are not as direct as those of hyaluronic acid. If your skin is only temporarily dehydrated without barrier damage, ceramides may not be as noticeably effective as hyaluronic acid.
Hyaluronic Acid vs. Ceramides: How to Choose
Since hyaluronic acid and ceramides each have their strengths, how do you choose the right ingredient for yourself? In fact, these two ingredients are not mutually exclusive but can complement each other.
–When to Use Hyaluronic Acid
- When the skin is temporarily dehydrated and needs quick hydration.
- When the skin is in a healthy state and only requires daily moisturization.
- When you want the skin to appear more plump and radiant.
–When to Use Ceramides
- When the skin barrier is damaged, leading to dryness, peeling, sensitivity, and other issues.
- When frequently exposed to dry environments, resulting in significant moisture loss.
- When you aim to fundamentally improve the skin’s moisture retention capability.
–Optimal Combination Strategy
For most people, combining hyaluronic acid and ceramides may be the best choice. Hyaluronic acid provides rapid hydration, while ceramides repair the barrier and lock in moisture. Together, they achieve a comprehensive skincare effect of “hydration + moisture retention + repair.” For example, in a daily skincare routine, you can choose a serum containing hyaluronic acid and pair it with a cream containing ceramides, satisfying both immediate hydration needs and long-term moisture retention and repair.
B2B: Where to Purchase Raw Materials
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a trusted supplier of cosmetic ingredients such as hyaluronic acid and ceramides.
We Offer:
- Hyaluronic Acid Powder: High purity, non-animal, non-GMO, cosmetic grade, medical grade, food grade, injectable grade.
- Ceramides: Purity >98%, enhances intercellular cohesion in the stratum corneum.
Enjoy bulk purchase discounts and contract pricing.
FAQs
Q: What is the Main Difference Between Hyaluronic Acid and Ceramides?
A: HA primarily works to attract and retain moisture. Ceramides are mainly used to build and repair the skin barrier.
Q: In Terms of Moisturizing Effectiveness, Which is Better: Hyaluronic Acid or Ceramides?
A: HA excels in immediate hydration and increasing skin moisture, providing quick moisture to the skin. Ceramides are more effective for long-term hydration and maintaining the skin barrier.
Q: For Sensitive Skin, Which is More Suitable: Hyaluronic Acid or Ceramides?
A: Ceramides are more suitable for sensitive skin because they can repair and strengthen the skin barrier, reducing damage from external irritants.
Q: Can Hyaluronic Acid and Ceramides Be Used Together?
A: Of course. Combining them yields better results.
Read more:
Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen: The Perfect Combination for Healthy Skin
Sodium Hyaluronate: Uses, Molecular Weight, Production and Derivatives
[i] Coderch L, López O, de la Maza A, Parra JL. Ceramides and skin function. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(2):107-29. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200304020-00004. PMID: 12553851.
The post Hyaluronic Acid vs. Ceramides: Which Works Better appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post What Ingredients Can Quickly Alleviate Alcohol Intoxication appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>Therefore, the true way to alleviate alcohol intoxication is to break down the acetaldehyde in the liver. Substances that can directly or indirectly help the body process acetaldehyde are considered effective in alleviating alcohol intoxication.
Dihydromyricetin, Pueraria Extract, Vitamin B Complex, Silymarin, etc., are ingredients that can directly or indirectly alleviate alcohol intoxication.
Dihydromyricetin: A Multifaceted Ingredient for Alleviating Alcohol Intoxication
Dihydromyricetin (DHM), a naturally occurring flavonoid, is widely found in many plants such as vine tea, bayberry bark, and grape seeds.
Dihydromyricetin promotes the metabolism and elimination of acetaldehyde through various pathways. Firstly, it significantly enhances the activity of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), accelerating the conversion of acetaldehyde to acetic acid, thereby reducing the accumulation of acetaldehyde in the body. This action not only alleviates discomfort caused by alcohol, such as headaches, nausea, and fatigue, but also reduces the toxic effects of acetaldehyde on the liver and other organs. Additionally, dihydromyricetin possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which help mitigate the oxidative stress and inflammatory responses generated during alcohol metabolism, protecting liver cells from damage.
Besides promoting alcohol metabolism, dihydromyricetin has been found to offer various other health benefits. It shows positive effects in antioxidation, anti-cancer, and protection of the cardiovascular and nervous systems.

Fig 1. Vine tea, the white is a flavonoid compound containing dihydromyricetin
Pueraria Extract: Comprehensive Relief from Alcohol Intoxication
Pueraria is a leguminous plant widely distributed in East Asia, including China, Japan, and Korea. It contains various health-beneficial active ingredients, such as isoflavonoids, puerarin, vitamins, and minerals.
Pueraria provides comprehensive relief from alcohol intoxication. Extensive clinical evidence shows that pueraria can alleviate alcohol intoxication, sober up, quench thirst, and protect against alcohol-induced liver damage.
Taking pueraria before drinking can protect the liver and stomach, enhancing alcohol tolerance. Consuming it during drinking can accelerate the metabolism of alcohol, reducing its damage to the heart and brain. After drinking, pueraria can relieve symptoms caused by alcohol, such as nausea, headache, and dizziness, thus reducing the severity of intoxication.
Moreover, pueraria not only alleviates alcohol intoxication but also aids in alcohol cessation. Modern studies have found that pueraria extract selectively inhibits human acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, significantly reducing the alcohol intake of heavy drinkers.

Fig 2. Pueraria Extract
Vitamin B Complex: Assisting Alcohol Metabolism
Vitamin B complex is a group of water-soluble vitamins. It includes various vitamins such as Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, etc.
Alcohol metabolism in the body primarily occurs in the liver and involves two main steps:
- Ethanol is converted to acetaldehyde.
- Acetaldehyde is converted to acetic acid.
Vitamin B complex, especially Vitamins B1, B2, B6, and B12, plays an auxiliary role in the alcohol metabolism process.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine): Participates in energy metabolism in the body, supports liver function, and helps increase the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, thereby accelerating the metabolism of ethanol and acetaldehyde.
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): Acts as a coenzyme in various redox reactions, helping to maintain the normal function of liver enzymes and supporting alcohol metabolism.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Involved in amino acid metabolism and the synthesis of neurotransmitters, helping to alleviate the negative effects of alcohol on the nervous system.
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) and Folic Acid (Vitamin B9): Play important roles in red blood cell production and DNA synthesis, helping to repair cell damage caused by alcohol intake.
By supporting energy metabolism and nervous system health, the Vitamin B complex helps alleviate post-alcohol fatigue, headaches, and nervous system discomfort. Additionally, supplementing with Vitamin B complex can help restore the depletion of these vitamins caused by alcohol intake, promoting the body’s recovery.

Fig 3. Vitamin B Complex
Silymarin: Providing Liver Protection
Silymarin is an extract from the seeds of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum), belonging to the flavonoid class of compounds. It has significant antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and liver-protective effects.
Silymarin is best known for its protective effects on the liver. It can stimulate the regeneration of liver cells, helping to repair damaged liver tissue. Silymarin also enhances the activity of the liver’s detoxification enzyme system, improving the liver’s ability to metabolize and eliminate toxins.
Although silymarin does not directly promote alcohol metabolism, it indirectly helps the body process and metabolize alcohol more effectively by protecting and supporting liver function. Silymarin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties reduce the damage acetaldehyde causes to liver cells, enabling the liver to handle alcohol and its metabolites more efficiently. Additionally, silymarin can enhance the activity of various detoxification enzymes in the liver, such as glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase, increasing the liver’s ability to metabolize and eliminate alcohol and other toxins.

Fig 4. Milk Thistle
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is an excellent supplier of herbal extracts. We provide Dihydromyricetin (DHM), Pueraria Extract, Milk Thistle, Vitamin B\C\D, etc. For more information about these materials, please contact us: GET A QUOTE.
Conclusion
The key to alleviating alcohol intoxication lies in accelerating the breakdown and metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby reducing the harm alcohol inflicts on the body. Ingredients such as dihydromyricetin, pueraria extract, Vitamin B complex, and silymarin help the body process acetaldehyde directly or indirectly, alleviate post-alcohol discomfort, and protect liver health.
However, the effectiveness of these ingredients varies among individuals and cannot completely offset the dangers of excessive drinking. Therefore, moderate drinking or abstaining from alcohol remains the best choice for protecting health.
FAQs:
Q: Can alcohol alleviating medicines completely eliminate the harm caused by alcohol?
A: No. Alcohol alleviating medicines can only relieve some discomforts and cannot completely offset the harm alcohol causes to the body, especially the dangers of long-term excessive drinking.
Q: Can silymarin be taken long-term?
A: Silymarin is generally considered safe, but you should consult a doctor before taking it long-term, especially if you are taking other medications.
Q: Is dihydromyricetin safe?
A: DHM is considered safe, but some users may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as diarrhea, nausea, or stomach pain after taking DHM.
Q: Does dihydromyricetin help with hangover?
A: Yes, dihydromyricetin (DHM) may help alleviate hangover symptoms. Studies suggest that DHM can accelerate the metabolism of alcohol, reduce the buildup of toxic byproducts like acetaldehyde, and protect the liver from alcohol-induced damage.
The post What Ingredients Can Quickly Alleviate Alcohol Intoxication appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen: The Perfect Combination for Healthy Skin appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>Hyaluronic Acid vs. Collagen: Performing Different Roles
Hyaluronic acid, also known as hyaluronan, is widely distributed in joint fluid, skin, and eyes. It is a high-level polysaccharide composed of repeating units of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine, and it is an important component of the extracellular matrix.
Collagen is a biological macromolecule primarily used to fill fine wrinkles and minor soft tissue defects. It is mainly distributed in bones, eyes, teeth, tendons, internal organs, and other areas. In the skin, it accounts for 70% of its composition, making it the most abundant protein in the human body.
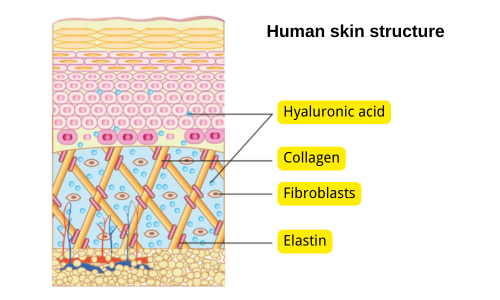
Fig 1. Human skin structure
In the structure of skin tissues, hyaluronic acid acts as a moisture reservoir and locks in moisture, while collagen affects the skin’s fullness.
–Hyaluronic Acid: The Skin’s “Natural Reservoir”
Hyaluronic acid acts like a “sponge” in the skin, quickly replenishing moisture.
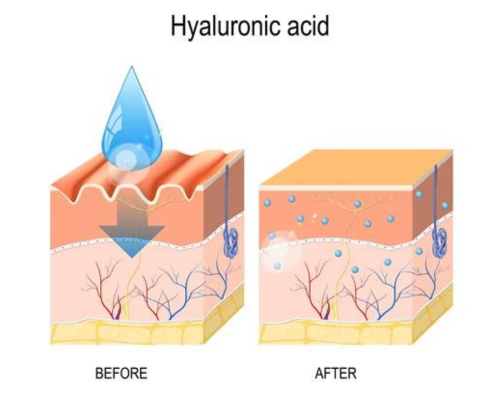
Fig 2. HA’s powerful moisturizing effect
- Core Function: Strong Hydration
Hyaluronic acid has an extremely high water-absorbing capacity, capable of absorbing 1,000 times its own weight in water, thereby improving dryness. A 2% pure hyaluronic acid aqueous solution can firmly retain 98% of moisture, making it the best natural moisturizer discovered, known as the Natural Moisturizing Factor (NMF).
- Anti-Aging Function: Filling Fine Lines
Hyaluronic acid can fill the fine lines on the skin’s surface, making the skin appear plumper and smoother. However, it does not directly enhance skin elasticity; it primarily keeps the skin youthful through hydration.
- Repair Function: Gentle Repair
Hyaluronic acid possesses gentle repair capabilities, promoting wound healing and making it suitable for sensitive or barrier-damaged skin. It also helps repair the skin’s natural barrier, enhancing its moisture-locking ability.
–Collagen: The Skin’s “Support Framework”
Collagen forms a network structure, an “elastic net” that supports the skin.
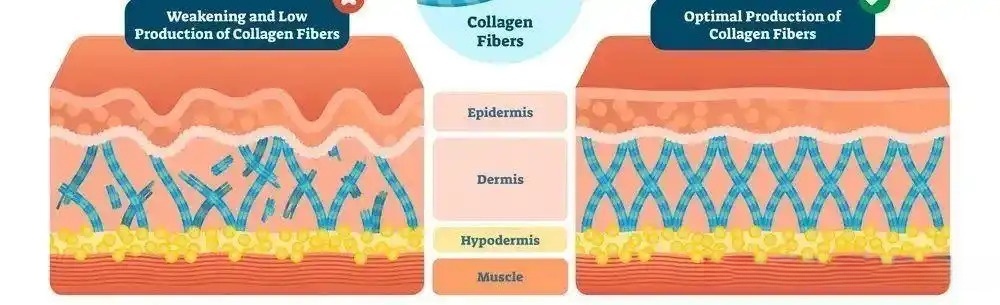
Fig 3. The supporting effect of the triple helix structure
- Core Function: Enhancing Elasticity
Collagen is the main component of the dermis, responsible for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. As age increases and this protein is lost, the skin gradually becomes loose and develops wrinkles. Supplementing collagen can help restore the skin’s support structure and enhance elasticity.
- Anti-Aging Function: Deep Anti-Aging
Collagen can improve the skin’s elastic fiber network from the deep layers, reducing wrinkles and sagging. Compared to hyaluronic acid, its anti-aging effects are more lasting but require long-term use to see significant improvements.
- Repair Function: Promoting Tissue Regeneration
Collagen can accelerate the repair of skin tissues, reduce scar formation, and is suitable for repairing deep injuries or post-surgical care.
–Summary
From a hydration perspective, hyaluronic acid is superior; from an anti-aging perspective, collagen can directly and quickly help restore skin elasticity. Both possess skin repair functions.
Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen: Complementing Each Other
In skin tissue, collagen affects skin elasticity, while hyaluronic acid acts as a moisture reservoir. Although there are differences between the two, they complement each other.
Both are indispensable in human skin.
- Lack of Hyaluronic Acid — Dryness, roughness, flakiness
- Lack of Collagen — Sagging, drooping, aging
As age increases, the body’s collagen content gradually decreases, weakening the skin’s support function. At this point, hyaluronic acid plays an important role. It can promote the synthesis and maintenance of collagen, thereby slowing the skin aging process.
Hyaluronic acid’s strong moisturizing ability can adsorb and lock a large amount of moisture inside the skin. This moisturizing effect not only keeps the skin hydrated but also reduces moisture loss, making the skin elastic. Hyaluronic acid can also form a protective film to prevent environmental stimuli and damage to the skin, while helping other active ingredients penetrate deeper into the skin.
The coordinated relationship between collagen and hyaluronic acid is very important in skin care. When collagen levels decline, the role of hyaluronic acid becomes particularly significant. It can improve skin elasticity and firmness by increasing collagen synthesis. At the same time, hyaluronic acid’s moisturizing function helps maintain the skin’s moisture balance, preventing dryness and moisture loss. Additionally, hyaluronic acid can promote the metabolism of skin cells, accelerating the process of skin repair and regeneration.
Where to Buy
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a trusted supplier of sodium hyaluronate and collagen peptides.
We offer:
- Sodium hyaluronate Powder: High purity, non-animal, non-GMO, cosmetic grade, medical grade, food grade, injectable grade.
- Collagen Peptides: Extracted using targeted enzymatic digestion technology and advanced membrane separation technology from animal tissues (fish scales, cow bones, chicken breast cartilage).
Enjoy bulk purchase discounts and contract pricing.
The post Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen: The Perfect Combination for Healthy Skin appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>